The term Internet of Things originated from the imagination of the intelligent home life in the book "The Road Ahead" written by Bill Gates, the founder of Microsoft Corporation in the United States in 1995. As the development of information technology was immature at that time, the Internet of Things did not attract much attention from the world. In 1998, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in the United States proposed the "Internet of Things" concept of the Electronic Product Code (EPC) system. In 1999, the director of the school’s Auto-ID Center Kevin Ashton (Kevin Ashton, later known as The father of the “Internet of Thingsâ€) based on the research of Radio Frequency IDenTIficaTIon (RFID), it is proposed that the sensing equipment connects to the Internet through radio frequency identification technology for information transmission and exchange, and achieves intelligent identification and operation management. Networking information network concept.
In recent years, as the development of related information technology has matured, the global Internet of Things network infrastructure structure has gradually taken shape, through the digital communication data acquisition and communication of various devices, and linking physical objects with digital information data, providing automatic control and management Value-added functions such as, detection, identification and services; how to build the Internet of Things world is still in the current state, as the chairman of Taiji Power Zhang Zhongmou said: "The Internet of Things is a big idea, but no company can Truly manage the entire ecosystem".
So, when more and more innovative technologies and applications are developed to promote the Internet of Things, what impact will it have on our lifestyle? What new business model will it bring? Especially for payment services, What are the impacts and opportunities? Various unknowns and imaginations are disturbing; this article intends to discuss the current application and development of the Internet of Things from the perspective of technological evolution, and to analyze the possible trends of the payment industry in the future under the framework of the Internet of Things Toward, provide reference.

(1) Definition of Internet of Things
Kevin Ashton’s earliest vision for the Internet of Things was: “Today’s information technology is so dependent on information generated by people that our computers understand thoughts rather than matter. If computers can do without our help, Knowing all kinds of information that can be obtained in the material world, we will be able to track and measure those substances, greatly reducing waste, loss and consumption. We will know when items need to be replaced, repaired or recalled, whether they are new or have expired The Internet of Things has the potential to change the world, just like the Internet, or even more far-reaching.†(Data source: Encyclopedia website). In other words, the ideal state of the Internet of Things is: the computer can reach the computer without human intervention. ) Communication with computers (things) to provide people with more convenient, comfortable and safe services and lives. Therefore, the European Union Radio Frequency Identification Technology Standard (CASAGRAS, CoordinaTIon and Support AcTIon for Global RFID-related Activities and Standardization) puts forward a practical definition: "Internet of Things" is a globalized network infrastructure, through communication data capture and Communication mechanism, linking physical or virtual objects, and further linking all objects together through specific mechanisms and Internet facilities, providing control, detection, identification and information exchange services.
(2), IoT environment
In order to achieve the ideal state of the Internet of Things, the International Telecommunication Union published the Internet of Things report "ITU Internet Reports 2005: The Internet of Things" in 2005, which proposed information technology practices and described the future Internet of Things environment as a "universal network society" ( Ubiquitous Network Societies, please refer to Figure 1 and Figure 2). It is announced that all target devices can be connected to the network through tag identification technology (such as RFID) or information equipment (called smart home life, please refer to Figure 3) anytime and anywhere; Constructing the aforementioned universal networked social life and creating the value of the Internet of Things, the International Telecommunications Union conceived an Internet of Things environment based on radio frequency identification technology labels and sensors, and aimed at the development process of Internet of Things creative ideas, product development, manufacturing and listing services. Provide a complete methodology and basic model for rapid expansion and application of various industries to build a more so-called smart home living environment. At the same time, through high-efficiency operation, it can increase production capacity, resource utilization, and improve the interaction between humans and the natural environment.
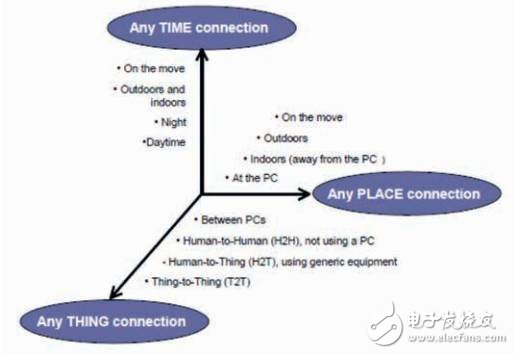
Figure 1 Data source for communications in the future IoT environment: International Telecommunication Union Internet Reports 2005: The Internet of Things
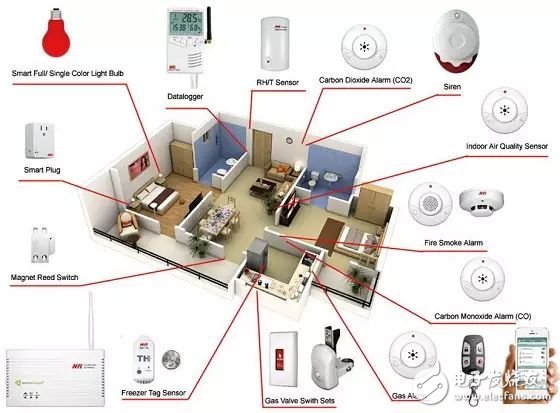
Figure 3 Smart home life
(3), IoT architecture standards
In order to achieve the ideal goal of a universal network society in the Internet of Things environment, it is necessary to construct a universal terminal equipment and network environment, including sensors with information processing capabilities, mobile terminal equipment, home smart equipment, monitoring system equipment, etc.; no information Static information objects with processing capabilities (such as RFID), personal wireless or vehicle intelligent communication equipment, etc., through various (long/short-distance) wireless or wired communication networks, to achieve object-to-machine communication applications (Machine to Machine" M2M", Machine to machine Application Integration "MAI") and material communication service "MaaS" (Machine to machine As A Service) functions to achieve high-efficiency and energy-saving manufacturing mechanisms and convenient, safe, and environmentally friendly smart life goals The basis for the development of the universal Internet of Things is to conceive a feasible architecture (Architecture) and its derived complete industrial ecosystem. In the world of Internet of Things operation, no single wireless or wired technology can effectively serve the overall architecture, and there is no Any unit can master all knowledge and technology or provide products and services without the assistance of other units. Therefore, under the framework of the Internet of Things, the collaborative operation mode (Collaboration) will become more and more important. Only through the collaborative operation of various units in the ecosystem can stable and reliable products or specific and feasible services be provided. The following starts with the IoT architecture and briefly explains how to shape the IoT architecture, and then specifically deploy the IoT environment infrastructure.
1. Networked Auto-ID architecture
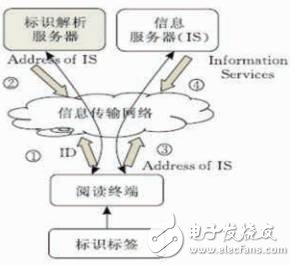
Figure 4 Networked Auto-ID architecture model
Networked Auto-ID Architecture is a concept proposed by the Auto-ID Laboratory of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1999. Its concept is to connect objects to the Internet through radio frequency identification (RFID), barcodes and other information sensing devices to achieve intelligence. Identify and manage goals. This kind of architecture consists of identification tags (such as magnetic stripe, barcode, two-dimensional barcode, radio frequency identification, etc.), identification label reading equipment (including magnetic stripe card reader, barcode scanner, optical reader, radio frequency reader, etc.) ), information transmission network (Internet, Intranet), logo resolution server and information server.
2. uIDIoT architecture
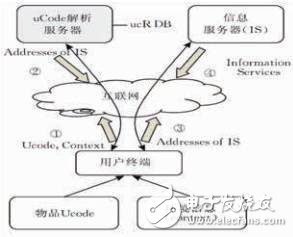
Figure 5 uIDIoT architecture
uIDIoT (Ubiquitous ID: Standard for Ubiquitous computing and the Internet of things) Architecture is the Internet of Things architecture planned by the Japanese non-profit standardization organization uID (Ubiquitous ID). Its goal is to "transmit Objects are identified through radio frequency identification and two-dimensional barcodes, and network sensors collect the surrounding context (Context), and adjust information services according to the collected environmental information.†Under the uIDIoT architecture, each object is assigned a unique object identifier Ucode (consisting of 128bits of data). In addition to obtaining the address of the object-related information server through Ucode query, it can also be identified with the object through network sensors The Ucode Relation (ucR) command is used to query the object identifier relational database (ucR DB) to obtain the addresses of other information servers related to the queried object.
3. USN architecture
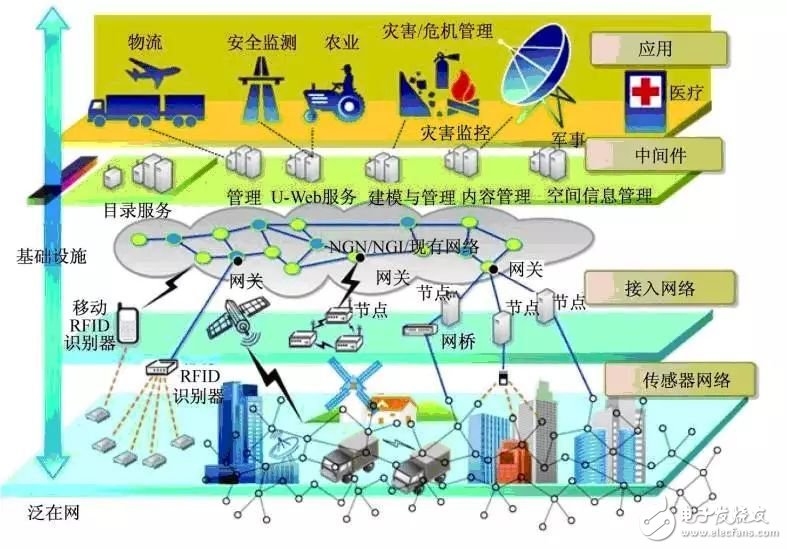
Figure 6 USN architecture
USN (Ubiquitous Sensor Network) Architecture is the “Next Generation Network Global Standard Initiative Meeting†(Next Generation Network Global Standard Initiative) held by the Korea Electronics & Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) in 2007 at the International Telecommunication Union in Geneva, Switzerland. Generation Network Global Standards Initiative, NGN GSI); the architecture adopts a layered concept, dividing the Internet of Things into five layers from bottom to top: sensor network layer (collecting and transmitting environmental information), access network layer (sensing Network and external communication), network infrastructure (next generation Internet), middleware/intermediary software layer (data access processing software) and application platform layer (applications in various industries). The USN architecture is currently widely used in Chinese industry and academia, but due to the lack of a unified definition of the communication interface between the various layers, the integrity of the architecture is relatively insufficient.
4. Physical Net architecture
Vicaire and others from the University of Virginia in the United States proposed an improved hierarchical Physical Net architecture for the more complex Internet of Things environment. From bottom to top, the service provider layer (the sensing device directly provides services) and the gateway layer (service collection) , Distribution, dynamic mobile management and real-time application configuration), coordination layer and application layer (application resource or cross-network management); Physical Net defines the communication interface standard between each layer-Remote Method Invocation (RMI), Physical Net Architecture is more feasible for realizing IoT system design.
5. M2M Architecture
The M2M architecture is a machine-to-machine (M2M Architecture) communication standard formulated by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI). It provides non-intelligent terminal devices with other smart terminal devices via mobile communication networks ( Intellectual Terminal (IT) or communication standards between systems, including service requirements, functional architecture and protocol definitions. The functional architecture of M2M is summarized as follows:
(1) Deploy M2M Service Capacity Layer (SCL) in devices, gateways and network domains with storage modules;
(2) The application in the device and the gateway communicates with SCL through the dIa (Deviceapplication interface) device application system interface;
(3) The applications in the network domain communicate with SCL through the mIa (M2M application interface) M2M application system interface;
(4) The device or gateway communicates with SCL through the mId (M2M to device interface) interface.
6. IoT A architecture
This is the research result of the 7th Framework Programme for Research and Technological Development (FP7) of the European Union. IoT A mainly solves the complex problems caused by large-scale, heterogeneous platform wireless and mobile communications in the Internet of Things environment , Is a tree-like networking structure reference model (Architectural Reference Model, ARM). It uses the M2M API to integrate different wireless communication protocols. It connects heterogeneous platforms through Internet IP and uses the concept of "reciprocating" The logical reference model is a structural system through architectural planning, and then the actual system is designed according to it, and the actual system operation status is fed back to the structural system, which is considered an important basis for the next round of reference model design.
(4) The development process of the Internet of Things environment
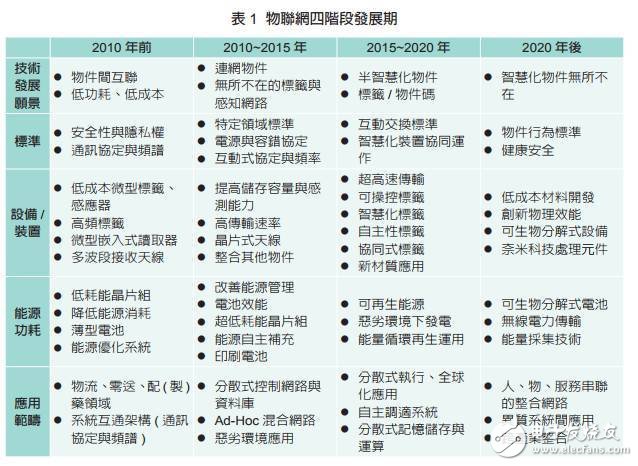
Table 1
The European Technology Platform on Smart Systems Integration (EPoSS)-RFID Working Group (European Technology Platform on Smart Systems Integration (EPoSS)-RFID Working Group) in the 2008 "Internet of Things in 2020" research report divided the development of the Internet of Things into four stages , And analyze and plan the development process of each stage, including technology development vision, standards, equipment/equipment, energy consumption and application scope (see Table 1).
(5) Application technologies related to the Internet of Things
The Internet of Things has a wide range of applications, and the technology that is more related to payment is selected. A brief summary is as follows:
1. Perception layer use technology
(1) Barcode recognition (Barcode, QRCode) uses barcodes or two-dimensional barcodes to mark the relevant information of the object, provide the scanning sensor to read the object's own information (Barcode), or further connect to the Internet to read the relevant information of the object. At present, this type of technology The development is quite mature, the cost is the lowest, and it is widely used in all walks of life.
(2), Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
This identification technology is mainly composed of a sensor (Reader) and a tag (Tag). It uses the sensor to emit radio waves to activate the RFID tag within the effective sensing range, and the sensor’s radio waves start the operation of the tag’s chip and respond to the sensor. . At present, RFID is widely used in China, such as financial cards, bus cards, high-speed ETC, etc.
(3), Near Field Communication (NFC)
NFC is mainly used for the communication and identification function between mobile devices (such as mobile phones) and other devices or mobile devices, providing different sensing operation modes such as point-to-point, card emulation or readers. At present, it is mainly used in mobile phone financial cards, credit cards, etc. field.
(4) ã€Wireless Sensor Network
This technology mainly provides the ability of objects to sense changes in the environment or the movement of objects, and transmit relevant sensing information through infrared, ultrasonic, brightness, temperature, humidity, pressure and other sensing components, as well as various network protocols.
(5), Embedded (Embedded) equipment
Various types of terminal devices, including mobile phones, amusement instruments, digital home appliances, etc., use embedded technology to combine software with the application of hardware devices to enable them to receive network messages and process information, or to add software computing functions to smart devices , So that it has the ability to receive, transmit and process information.
2. Network layer communication technology
(1) Local area network: such as RFID, Bluetooth, Beacon, infrared transmission, Zigbee, WiFi and other technologies.
(2) External network: such as 3G/4G wireless communication, WiMAX and other technologies.
3. Application layer development
Covers a variety of innovative application integration services, such as wearable devices, smart homes, smart low-carbon, smart business, smart grid, smart transportation, etc., as well as various big data application technologies derived from a large amount of information brought by the Internet of Things environment. Network system service companies such as Google, Apple, and Samsung are optimistic about the huge business opportunities brought by the Internet of Things, and respectively launched the Internet of Things operating system, such as Google launched Brillo based on the Android platform; Apple launched HomeKit for iOS; Windows 10 for Microsoft Windows IoT Core system, etc., and even ARM, a large processor silicon intellectual property (IP) manufacturer, has combined with Cortex-M device controller devices to launch the Internet of Things operating system mbed OS, which provides various industrial applications of Internet of Things technology to develop various product platforms (such as Smart home products Nest, smart watches Pebble). In addition, major system manufacturers such as Google and Apple are also gradually establishing their own IoT industry ecosystem with the help of building an IoT architecture.
Third, the development trend of Internet of Things payment applicationsWith the rise of the Internet of Things architecture, a large amount of information is rapidly transmitted through the network, which is expected to have a major impact on the existing business operation model, especially through the physical object perception and interaction mode, which completely integrates network virtual services and physical business operation process mechanisms. To make the interactive application of traditional e-commerce gold flow, logistics and information flow closer, I would like to briefly analyze the future development trend of the application of the Internet of Things in payment services for reference.
(1) Consumption and payment integration service model
In the past, the financial payment mode was mainly a passive service mode. Regardless of one-way fund transfers such as withdrawals, remittances, and transfers, or after the consumer completed the consumption behavior, the payment transaction request was initiated, and the financial institution renewed the relevant transaction according to its request. Processing services, all of these, consumers have less coupling with payment services due to consumption or fund transfer. In the environment of the Internet of Things, through the physical object perception and interactive service mode, consumption or business behavior and payment service information will be closely integrated. For example, the QR Code is used to provide online payment service function mode, and consumers can scan the intended purchase through the smartphone App The QR Code of the product is directly connected to the back-end system of the store to complete the relevant payment process. The purchased product can be received at home soon. The overall cash flow, logistics, and information flow are automatically connected; in addition, the QR Code is also applied to the payer Identity recognition, such as bus tickets, movie tickets, vending machines, etc., when consumers use the QR Code provided by the merchant to link to the service website, after the consumer completes the payment, the merchant information system will return the buyer's proof of purchase (that is, provide another A QR Code), as a proof for consumers to redeem the purchased subject.
(2) Contextual payment service model
The Internet of Things environment uses sensing devices such as RFID and NFC, and uses mobile APP network sensing combined with LBS (Location Based Service) technology to confirm the location of consumers (payers and payees), the surrounding environment and their own status in real time. It can ensure the flow of funds and personal safety of the payer, and reduce losses or risks. In terms of consumer services, mobile phone operators (such as Apple or PayPal) use low-power Bluetooth device Beacon technology (such as iBeacons or PayPal Beacon) to communicate with customers’ mobile phones. When customers enter the (physical) cooperating with operators (such as PayPal, Apple) ) At the store, Beacon will actively connect with the customer’s mobile app downloaded from the operator in advance, and notify the user through the mobile phone of the online message. When the customer is ready to purchase items, they only need to prompt the clerk to use the operator’s payment tool to make the payment. That is, the payment transaction is automatically initiated for processing. This type of payment service can bring different convenient experiences and personalized services to customers. In addition, the cost of deploying Beacon equipment by merchants is low, and customers can get the latest store discount information and enjoy simpler and faster payment services. Based on the big data computing technology of consumer information, financial institutions analyze consumer transaction history records, and use the Internet of Things perception environment to confirm the real-time status of consumers, estimate consumer needs and market in time, which can effectively increase the business of financial institutions. Close.
(3) Biometric payment mode
Traditional authentication methods such as card payment tools and passwords will gradually shift to a payment service model based on biometric identification technology due to the rise of the Internet of Things environment. "Biometric identification" mainly relies on biometric technology to determine the identity of a customer based on the human body’s physiological organs (such as face, eyes, fingerprints, etc.) and behavioral characteristics. Financial institution accounts perform payment authorization operations online. This mode of payment service can be completed without other transaction vouchers (such as payment cards) through the user's biometric control mechanism, called "biological payment".
At present, some commercial banks and China's third-party payment agency Alipay have launched such services. This emerging payment model will gradually expand its application areas in the future.
(4) Internet of things (smart) bank payment services
Financial institutions are the core of the payment business. Under the development trend of the Internet of Things, financial institutions must transform from a traditional static financial service to a dynamic technology financial service model in order to actively grasp the trends and needs of consumers and confirm with the perception function of the Internet of Things Consumers’ location, surrounding environment, etc., and then through traditional financial services based on consumer credit, service life cycle and the big data of the Internet of Things environment and other intelligent analysis, real-time provide consumers with necessary and interesting products and services, and create new Payment opportunities. For example, for consumer credit loans, traditional financial institutions often decide whether to grant loans or interest rate levels based on their transactions with consumers and related credit investigations. Therefore, when consumers apply for loans and approve payment after review, this process may be costly Time, there are already pure online banks using IoT environment awareness and big data technology to conduct smart analysis of consumers’ online behaviors, identities, occupations, personal connections, credit history, and performance capabilities, etc., to verify loans and make payments in real time Consumer payments. In addition, some financial institutions integrate the enterprise's mortgage/guarantee or products and other movable property information through the application of the Internet of Things perception function to integrate with the enterprise lending system, so as to grasp the mortgage/collateral or shipment status of the lending enterprise in real time, which can further integrate the enterprise The process of manufacturing or operating activities quickly completes online financing operations, pays corporate financing, and achieves real-time monitoring of mortgage debt status and reduces lending risks.
(5) Demand for payment services derived from the sharing economy model
The futuristic master Jeremy Rifkin described in the book "Internet of Things Revolution": "The Internet of Things is about to bring about a society where everything is free? Except for the current publishing, communications and entertainment industries, the future, The goods and services of manufacturing, energy, education, and more industries will also enter a "free" state. By then, what kind of dramatic changes will the business operations, people's work, and market economy face? The market economy is gradually declining. , The sharing economy has become the mainstream?? "Access" surpasses "ownership", "cooperation" overrides "competition", and "sharing" completely replaces "transaction". As a result, the GDP, which has always been used to measure economic performance, has been declining. The rules and models of the market economy will be completely subverted.†It is expected that the “sharing economy†will create huge commercial value in product services and market recirculation models; in addition, according to PricewaterhouseCoopers (PWC) According to statistics on the economic scale of sharing models of cars or houses such as Uber and Airbnb, the output value created in 2014 was about 15 billion U.S. dollars, and it will grow to 335 billion U.S. dollars within ten years. It can be seen that the future sharing economy business model and its derivative payment service demand cannot be accommodated. Underestimate.
Fourth, the problems faced by the application of Internet of Things paymentAlthough the Internet of Things can bring us more convenient and comfortable services and life, and at the same time promote industrial innovation and reform, because the relevant supporting measures and management mechanisms have not been perfected, it will become a major challenge for the future development of the Internet of Things. described as follows:
(1) Diversified standards for technology application development are not unified
As the related technologies of the Internet of Things system are widely used, and there are heterogeneous information equipment or network environments, it is difficult to unify the technical standards, and it is easy to cause poor information operation efficiency. In addition, the provision of financial payment services based on the Internet of Things architecture does not seem to have a more concretely formed unified standard for the real-time, accuracy of transaction information, and specifications for cross-institutional/industry information data exchange. This will be the follow-up promotion of Internet of Things payment, etc. The first problem that the service must overcome.
(2) The application does not reach economic scale and cannot reduce operating costs
The biggest feature of the application of the Internet of Things technology is the digitization and digitization of objects. The construction of the Internet of Things payment environment must invest in costs including object tags, sensing receiving equipment, application integration equipment, communication networks, and back-end business information processing platforms. Most of the systems are of a trial operation nature, and have not reached the full application stage, and the share ratio and transaction volume are still not significant. It must rely on time to gradually expand the service scope to achieve economic scale. Therefore, the relevant operating costs cannot be effectively reduced in the short term, which will affect the Internet of Things The promotion of the system.
(3) Information security needs to be strengthened
In the Internet of Things environment, information devices are closely connected in series. However, the current data transmission or information processing mechanisms between devices still do not have complete information security protection measures. For example, unauthorized organizations/individuals or objects conduct RFID tags. Reading and writing, personal data protection, privacy and security issues, and even illegal tracking, stealing of goods or confidential information, seeking improper benefits or deliberate sabotage, are all important considerations for security. In addition, IoT sensing devices are connected to the back-end information system through the Internet, and they will also be attacked by viruses and hackers, causing the system to be inoperable; therefore, strengthening information security will become an important goal in promoting IoT payment services.
(4) Management mechanism has yet to be improved
In the operating environment of the Internet of Things, communication between objects and objects will become the norm. How to strengthen the use or control of the resources of the objects, the protection of personal data, the effective integration of Internet of Things information, and the cross-organization trust mechanism will gradually face challenges. , Becoming an important key to the successful expansion of the future Internet of Things payment business.
V. ConclusionAt present, various industries are in full swing with the development of IoT applications, which is expected to create a new pattern for the payment industry. As various technical and operational problems are gradually overcome, more and more mature IoT payment application models will be launched one by one. Facing the rise of the Internet of Things payment business in the future, I would like to briefly explain the observation experience.
(1) Improving Internet infrastructure is a necessary prerequisite
The IoT payment model is more complex than the traditional payment service ecosystem and cannot be done by a single institution alone. According to the IoT forecast report of Gartner, a US information technology research and consulting agency, the number of IoT devices in use worldwide will reach 4.9 billion in 2015 This is an increase of 30% over 2014 and will grow to 25 billion by 2020. In order to meet the new Internet identification code (IP) demand for the huge number of Internet of Things devices in the future, the upgrade of the Internet communication protocol of each unit is an urgent issue.
(2) "Transaction security" is the most important pillar of IoT payment
Transaction security is an important item to help the payment business. Although the Internet of Things technology continues to advance, how to balance transaction security and ease of use will be the key to the successful promotion of Internet of Things payment services. Therefore, a complete risk management mechanism is maintained at all times, technical standards are continuously improved, and improper storage or transmission of transaction data is avoided. This effectively reduces operational risks and strengthens transaction security, thereby increasing customer trust and loyalty, and paying for the Internet of Things. Lay the foundation for long-term development.
(3) The communication model between things and things expands the development space of payment business
The biggest feature of the Internet of Things is to successfully promote the automatic operation mechanism of computers (things) and computers (things), successfully realize the communication mode between things and things without human intervention, and provide people with more convenient, comfortable and safe services. And life, in the future, due to the emergence of the Internet of Things and the automatic operation mechanism of things, the payment industry will extend the service field, providing perception functions through the Internet of Things, collecting customer information and conditions, and quickly responding or providing customers through the big data analysis model The service will further obtain more customer service opportunities, drive new payment demands and business growth, and expand the scope and imagination of payment services.
(4) Complementarity between emerging payment services and traditional payment services
As the development of emerging technology drives new thinking and operating models, it has had unprecedented impact on traditional financial institutions. Recently, the term “technological finance†has attracted more and more attention internationally, prompting financial institutions to accelerate the pace of innovation, and domestic financial institutions will also Rapidly develop towards digital technology and finance. It is expected that the Internet of Things payment will become a new model for financial institutions to serve customers in the future. At the stage of promoting the development of new payment services, traditional payment tools will still be bulky in the short term. In view of the volatile and complex needs of consumers, financial institutions continue to provide diverse, Efficient and safe payment service options, differentiated strategies to differentiate the industry with competitive advantages, attract consumers. While developing emerging payment services, traditional payment tools can still coexist on the principle of complementarity, strengthen the analysis of customer group transaction habits, preferential methods, store sales behavior, etc., give full play to the advantages of IoT technology, provide customized services for consumers, and create Higher added value.
The Lifepo4 Sla Battery Replacement consists of advanced lithium iron phosphate cells that offer a long-lasting and reliable power output. With its high capacity and energy density, this battery pack can conveniently handle heavy loads during extended periods. Compared to the traditional lead-acid batteries, the Lifepo4 Sla Battery Replacement comes with robust features such as a deep battery cycle, faster charging time, lower self-discharge rate, and extended life cycle. It delivers a safer and cleaner energy source that is free from toxic substances, making it an eco-friendly product.
Sla Battery Replacement,Lifepo4 Battery Energy Storage System,Replacement Batteries For Solar Energy Storage,Replacement Batteries For Golfcart
JIANGMEN RONDA LITHIUM BATTERY CO., LTD. , https://www.ronda-battery.com