Color TV system
At present, there are three types of color TV systems in the world: NTSC system, PAL system and SECAM system.
(1) NTSC
The NTSC (NaTIonal Television Systems Committee) color television system is a color television broadcasting standard defined by the National Television Standards Committee in 1953, and is called orthogonal balanced amplitude modulation system. Most Western Hemisphere countries such as the United States and Canada, as well as China's Taiwan, Japan, South Korea, and the Philippines, adopt this system.
The main characteristics of the NTSC color television system are:
525 lines / frame, 30 frames / second (29.97 fps, 33.37 ms / frame).
Aspect ratio: the aspect ratio of TV pictures (4: 3 for TV; 3: 2 for movies; 16: 9 for high-definition TV).
Interlaced scanning, one frame is divided into 2 fields, 262.5 lines / field.
At the beginning of each field, 20 scan lines are reserved as control information, so there are only 485 lines of visible data. Laserdisc is about 420 lines, S-VHS is about 320 lines.
Each line is 63.5 microseconds, and the horizontal retrace time is 10 microseconds (including a 5 microsecond horizontal sync pulse), so the display time is 53.5 microseconds.
Color model: YIQ.
The total number of lines in a frame of image is 525 lines, and it is scanned in two fields. The line scan frequency is 15750 Hz and the period is 63.5 μs; the field scan frequency is 60 Hz and the period is 16.67 ms; the frame frequency is 30 Hz and the period is 33.33 ms. The number of scanning lines per field is 525/2 = 262.5 lines. Except for the two-field field retrace, the actual number of lines transmitted is 480 lines.
(2) PAL
Due to the shortcomings of the color distortion caused by the phase sensitivity of the NTSC system, Germany (then West Germany) formulated the PAL (Phase-AlternaTIve Line) color television broadcasting standard in 1962, called the progressive phase-inverting quadrature balanced amplitude modulation system. Some Western European countries such as Germany and the United Kingdom, as well as countries such as China and North Korea, adopt this system.
The main scanning characteristics of the PAL television system are:
625 lines (scanning lines) / frame, 25 frames / second (40 ms / frame);
Aspect ratio (aspect raTIo): 4: 3;
Interlaced scanning, 2 fields / frame, 312.5 lines / field;
Color model: YUV.
The total number of lines in a frame of image is 625, which is scanned in two fields. The line scan frequency is 15625 Hz and the period is 64 μs; the field scan frequency is 50 Hz and the period is 20 ms; the frame frequency is 25 Hz, which is half of the field frequency and the period is 40 ms. When sending a TV signal, the time to transmit the image in each line is 52.2μs, and the remaining 11.8μs does not transmit the image, which is the reverse time of the line scan. It is also used for line synchronization and blanking. The number of scanning lines per field is 625/2 = 312.5 lines, of which 25 lines are used for field retrace and no image is transmitted. The number of lines for transmitting images is only 287.5 lines per field, so only 575 lines per frame have images displayed. Figure 07-03-2 shows a black and white TV signal with a line period. The color TV signal is similar to it.
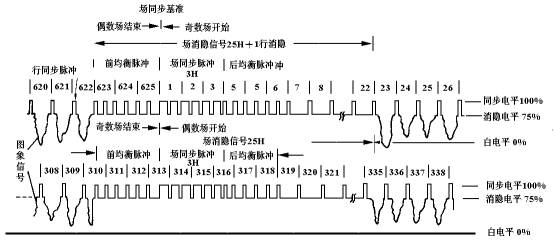
Figure 07-03-2 A line period of TV signal (black and white TV system)
(3) SECAM
France has formulated the SECAM (French: SequenTIal Coleur Avec Memoire) color television broadcasting standard, called sequential transmission color and storage system. About 65 countries including France, the former Soviet Union, Eastern Europe and the Middle East adopt this system. This system is similar to the PAL system, the difference is that the chrominance signal in SECAM is frequency modulation (FM), its red difference (R'-Y ') and blue difference (B'-Y') two chrominance signals It is transmitted in line order. The image format is 4: 3, 625 lines, 50Hz, 6MHz TV signal bandwidth, and the total bandwidth is 8MHz.
The main characteristics of the above three TV systems are shown in Table 07-03-1 and Table 07-03-2.
Table 07-03-1 Sync signal of color TV
TV format | PAL | NTSC | SECAM | |
water level set Time (μs) | Line cycle (H) | 64.0 | 63.55 | 64.0 |
Blanking width | 11.8 | 10.8 | 11.8 | |
Sync width | 4.7 | 4.7 | 4.7 | |
Front shoulder | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | |
Color burst starting point | 5.6 | 5.1 | — | |
Burst width | 2.25 | 2.67 | — | |
Equalized pulse width | 2.35 | 2.3 | 2.35 | |
vertical (field) Synchronize | Field sync pulse width | 27.3 | 27.1 | 27.3 |
Blanking width | 25H | 20H | 25H | |
Number of balanced pulses | 5 | 6 | 5 | |
Field sync pulse number | 5 | 6 | 5 |
Table 07-03-2 International Standards for Color Television
TV format | PAL GID | NTSC | SECAM |
Line / frame | 625 | 525 | 625 |
Frame / second (field / second) | 25 (50) | 30 (60) | 25 (50) |
Line / second | 15625 | 15734 | 15625 |
Reference white light | C white | D6500 | D6500 |
Sound carrier frequency (MHz) | 5.5; 6.0; 6.5 | 4.5 | 6.5 |
γ | 2.8 | 2.2 | 2.8 |
Color sub-carrier frequency (Hz) | 4433618 | 3579545 | 4250000 (+ U) |
Color modulation | QAM | QAM | FM |
Brightness band (MHz) | 5.0; 5.5 | 4.2 | 6.0 |
Chrominance bandwidth (MHz) | 1.3 (Ut) | 1.3 (I) 0.6 (Q) | > 1.0 (Ut) |
In order to meet the compatibility of color TV and black and white TV, it is necessary to transmit the luminance signal Y and two color difference signals U and V at the same time under the condition of the original black and white TV channel bandwidth. Since the resolution of human eyes for color details is lower than the resolution of brightness details, color difference signals U and V can be transmitted in a narrower frequency band than the brightness signal. In China's PAL / D color TV standard, the bandwidth of brightness Y It is 6MHz, and the bandwidth of U and V is 1.3MHz, which is a compromise between color details and brightness details.
Ring Type Connecting Terminals
Ring Type Connecting Terminals,Terminals,Connecting Terminals
Taixing Longyi Terminals Co.,Ltd. , https://www.longyicopperterminals.com