AMOLED

AMOLED is actually the abbreviation of AcTIve Matrix Organic Light EmitTIng Diode, the core is still in Light EmitTIng Diode, which is LED. Although LEDs are more common in everyday life, in the screen, each LED is very small in size and is divided into three sub-pixel groups of red, green and blue, and then different colors are formed, and the sub-pixels are arranged. The way will also affect the entire display.
The O in AMOLED stands for Organic, which is "organic". Simply put, a series of organic thin film materials are used between the positive and negative electrodes to achieve the purpose of illuminating.
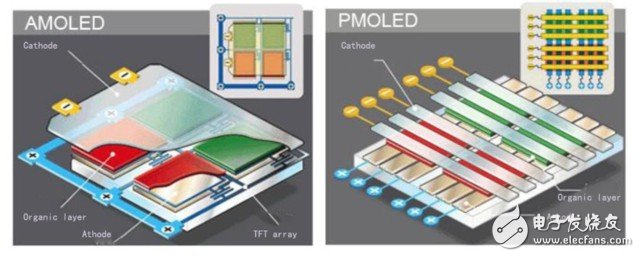
Finally, AM stands for AcTIve Matrix, which is relative to the Passive Matrix and refers to the way each OLED pixel is driven. In the Passive Matrix, the control of each pixel is realized by a complex electrode network to achieve charge and discharge of a certain pixel. In general, the Passive Matrix is ​​controlled at a relatively slow speed and has a slightly lower control precision. Unlike the Passive Matrix, the Active Matrix has a TFT and capacitor layer on each LED so that when a row is energized to activate the intersecting pixel, the capacitor layer in the pixel can be refreshed between refreshes. Maintaining a state of charge allows for faster and more accurate pixel illumination control.
The Super AMOLED claimed by Samsung is essentially the same as AMOLED. It only implements the touch layer in the display layer, so there is no need to add an additional touch layer, which can reduce the thickness of the entire screen module.
The main advantage of OLED screens is the high degree of controllability of the pixels, each pixel can be independently switched to achieve purer black and higher contrast. In addition, turning off unnecessary pixels while displaying a picture can also reduce power consumption. At the same time, since the number of layers inside the screen module is small, the light transmittance is also better, which is advantageous for achieving higher brightness and a wider viewing angle.
Compared with LCD, OLED screen can be made very thin, which is very suitable for mobile devices such as mobile phones. In addition, due to the lack of a hard backlight layer and the maturity of flexible plastic substrates, OLEDs also have great advantages on flexible screens, creating more possibilities for future mobile devices and even wearable devices.
LCD
After talking about AMOLED, let's talk about LCD. The LCD is called Liquid Crystal Display, and the illumination method is very different from the AMOLED screen. Unlike AMOLED screen pixels, which can be independently illuminated, all pixel illumination of an LCD screen relies on a uniform backlight layer. Of course, for some large-size LCD screens used on some TVs, multiple light sources may be equipped to reduce power consumption.
Strictly speaking, there is no wavelength corresponding to white light in the world, and white light is only a mixed light of multiple colors of light. For this reason, the LCD can only produce a white backlight by means of backlight + phosphor, and the most common combination is blue backlight + yellow phosphor.
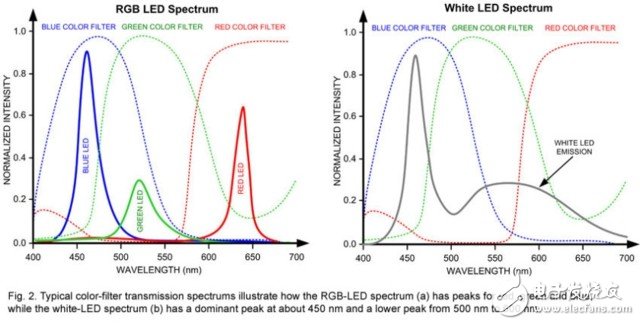
The white light generated by the backlight layer will convert the fully polarized light into linearly polarized light with uniform vibration direction, and then pass through the liquid crystal molecular layer, and according to different voltages, the liquid crystal molecules will have different twist angles, thereby Polarize the white light, twist the direction of the vibration, then generate different colors through the red, green and blue filters, and finally pass the second polarizing layer (perpendicular to the first layer) to control the light intensity. Finally, Different colors are realized by the combination of the intensity of light of three different colors of red, green and blue.
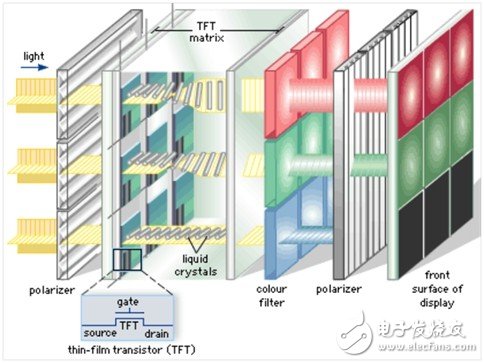
Similar to OLED, the LCD driver can be divided into Active Matrix and Passive Matrix. Currently, most LCD screens on mobile phones use Active Matrix.
AMOLED vs LCD
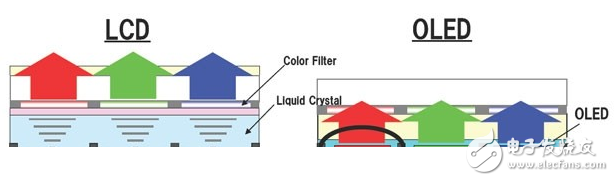
The biggest difference between AMOLED and LCD screen look-and-feel is that AMOLED generally has this wider color gamut, which can display more colors, and the displayed image will be more convenient. In addition, the AMOLED screen has a higher saturation when displaying blue and green, so the early AMOLED screens are often criticized for color inaccuracies and colors that are too bright. Compared to AMOLED screens, LCD screens typically overcompensate red and suppress green at the same time. Although the LCD screen color gamut does not have a wide range of AMOLED screens, it is actually closer to the standard RGB color gamut used for video and photo editing.
And if you do a detailed inspection of some AMOLED screen phones and some LCD screen phones, you can also see some differences. For example, although the screens are all from Samsung, the color gamut range of the BlackBerry Priv and Galaxy Note 5 is still slightly different, and the difference from the LG V10 using the LCD screen is more obvious. It is not difficult to see that in addition to the material of the screen itself, the adjustment of various manufacturers also has an impact on the color of the screen.
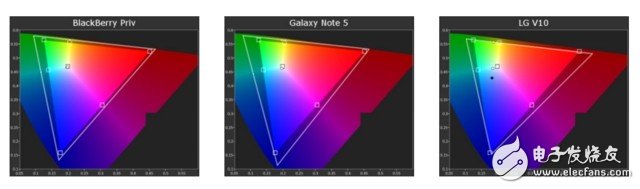
In addition to the color gamut, color registration is also a very important indicator of evaluation. From last year's test, it can be found that the color calibration performance of the AMOLED screen is very good, especially when the white color is displayed, the white color displayed by the BlackBerry Priv and the Galaxy Note 5 is very close to the actual white color, and the LCD screen usually has a bluish or It is green. Of course, considering that LCD screens usually use a blue backlight, it is not surprising that this result occurs.

In addition, in addition to being not dominant in weight, the backlight layer is not completely closed due to the use of a backlight layer, and the LCD screen is also inferior in terms of light leakage and low contrast. The AMOLED screen has different life cycles of RGB pixels. As the usage time increases, color drift may occur, and the LCD does not have such a problem.
Which is better?
LCD and AMOLED can be said to have their own advantages and disadvantages, and with the continuous optimization of LCD technology and the continuous improvement of AMOLED technology, in fact, in some high-end mobile phones, the gap between LCD and AMOLED is very small, not enough for everyday The use constitutes a huge impact. However, the advantages of OLED screens in terms of power consumption, thickness and display efficiency have gradually become prominent, and the cost is gradually decreasing, so it is more likely to become the future of the display industry. At the same time, LCD screens may be slowly squeezed into the low-end market.
Although it is known for its LCD technology, LG has also done a lot of research and development work in the field of OLED. It is estimated that by 2022, the market valuation of AMOLED screens will reach 30 billion US dollars, which is twice as large as now, and the application of curved screens may further promote the development of AMOLED screens.
N/Ph Silicon Wafer,Silicon Wafers Notch,Silicon Wafers Box,N Type Prime Si Wafer
Zoolied Inc. , https://www.zoolied.com