"Parameter measurement" is a great tool for oscilloscopes to analyze waveforms. Engineers can easily obtain various parameters without turning on the cursor. But there are also engineers who are a little worried: how does the oscilloscope guarantee the measurement accuracy? This article will take you step by step to understand the algorithm behind oscilloscope parameter measurement.
The ZDS series oscilloscope provides a very rich measurement function, with up to 51 measurement items. Most of the problems encountered by engineers during use are due to insufficient understanding of the details and principles. Here are the contents to take you step by step to dig deeper and solve your doubts.
1. How to use parameter measurement
It is relatively simple to open the measurement, remember two points:
1. Which channel do I want to measure?
2. What do I want to test?
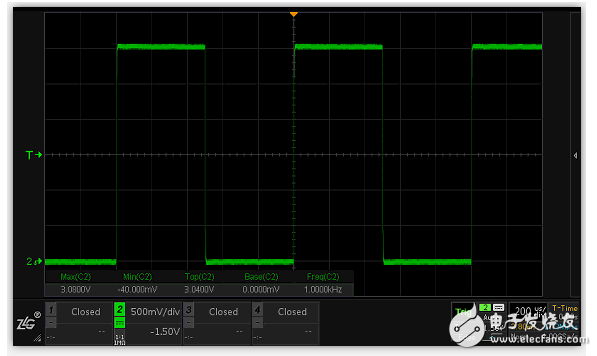
Figure 1 Open measurement
Summary: There are as many as 51 measurement items, and 24 measurement items can be displayed on the same screen.
2. Analysis of parameter measurement algorithm
The items measured in the oscilloscope can be roughly divided into two categories, one is related to voltage, such as maximum value, minimum value, top value, bottom value, etc. The other is related to time, such as frequency, period, rise time, fall time, duty cycle, etc. The top value and the bottom value are two very important measurement items, which are the basis of time measurement.
Measurements related to voltage are relatively simple. The maximum value (Vmax) and minimum value (Vmin) can be found by traversing all sample points. To solve the top value (Vtop) and bottom value (Vbase), it is necessary to map all the sample points first, and then find the voltage value with the greatest probability of occurrence.
Top value (Vtop): The voltage relative to the maximum probability of the upper part of the waveform, and the probability reaches more than 5% of the total number of sample points.
Bottom value (Vbase): Relative to the maximum probability voltage at the bottom of the waveform, and the probability reaches more than 5% of the total number of sample points.
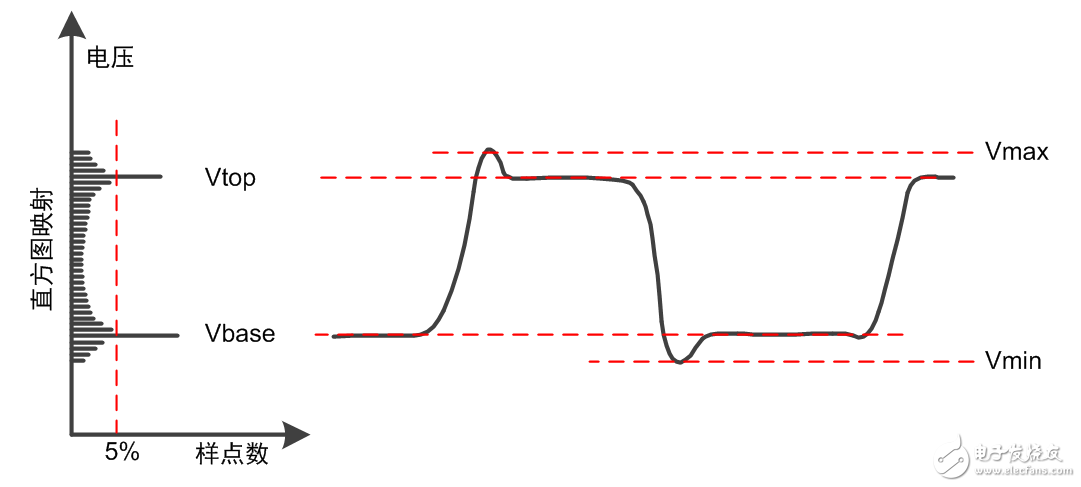
Figure 2 Measurement of voltage related items
For time-related measurement items, you need to use the top value (Vtop) and the bottom value (Vbase), and then use Vtop and Vbase to calculate the position of the three threshold lines of high, medium and low, and finally find the intersection of the threshold line and the waveform, you can get the time correlation The measurement results are shown in Figure 3. The positions of the three threshold lines of high, medium and low are adjustable, and the default values ​​are 90%, 50%, and 10%.
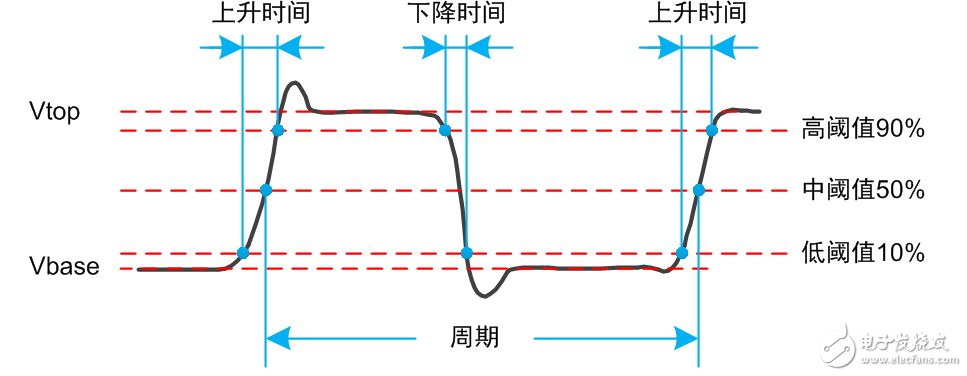
Figure 3 Measurement of time-related items
Summary: There are some special waveforms (such as sine waves) that will fail to solve Vtop and Vbase (with a probability of less than 5%). At this time, Vmax and Vmin will be used as the new top and bottom values, and will be in the Vtop and Vbase. After the value, append? Number is displayed to indicate abnormality, as shown in Figure 4.
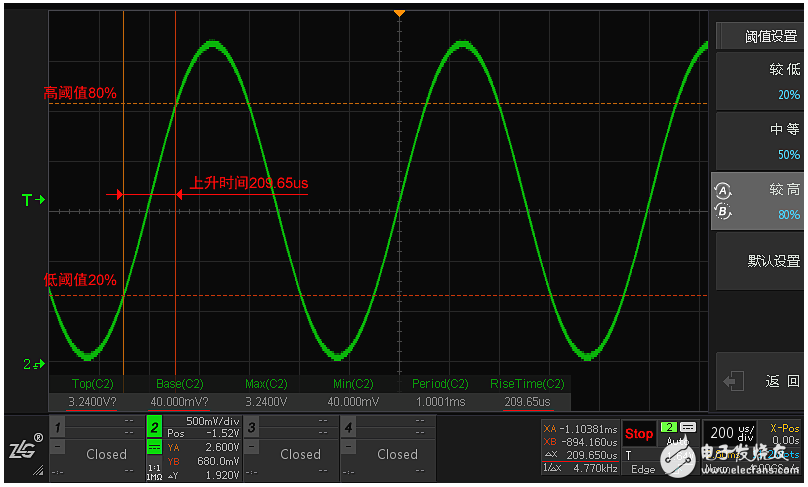
Figure 4 Top value, bottom value and maximum value, the minimum value is the same
3. Measurement and statistical algorithm analysis
The principle of measurement and statistics is simple. We must first understand a concept. The same measurement item may be encountered multiple times in the same measurement, such as a period. A waveform may have N periods. In this way, a new question arises. Which period of the waveform corresponds to the measurement result of the period? In order to solve this non-correspondence problem and make the measurement results more meaningful, we use 6 kinds of values ​​in statistics to describe the measurement results, respectively as follows:
Current value (Current): indicates the first measured value, corresponding to the position â‘ in Figure 5.
Maximum value (Max): indicates the maximum value among all the measured values, corresponding to the position of â‘¡ in Figure 5.
Minimum value (Min): indicates the minimum value among all the measured values, corresponding to the position â‘¢ in Figure 5.
Average (Avg): Represents the accumulated average of all measured values, corresponding to the accumulated average of the three positions in Figure 5.
Standard deviation (Stdev): Represents the standard deviation of all measured values, corresponding to the standard deviations of the three positions in Figure 5.
Count: indicates the number of measured values, corresponding to the three positions in Figure 5.
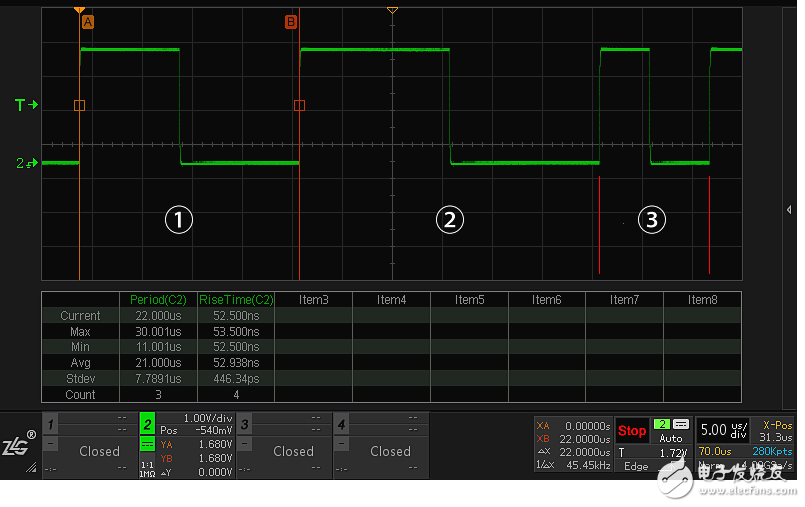
Figure 5 Measurement and statistics function cycle
Summary: The measurement statistics function is closed by default and can be opened in the menu. When the statistics is off, only the current value (Current) is displayed. When the statistics is on, 6 types of statistical results are displayed. The positive pulse width statistics function is used in Figure 6, and the maximum pulse width can be calculated as 3.028us, and the number of pulses is 42.
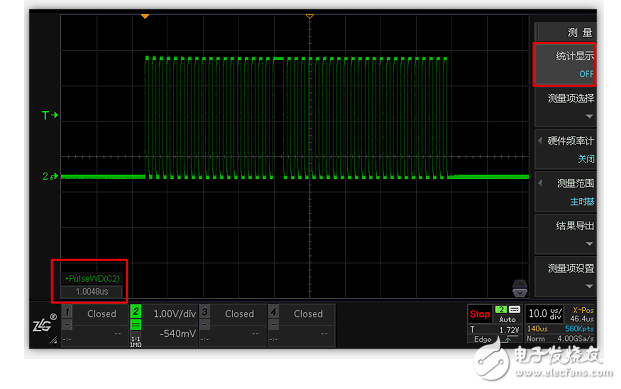
Figure 6 Statistics function can be manually turned on or off
Four, custom measurement range
When using measurement, a problem often encountered is that there are more waveforms captured, but I only want to measure and analyze a part of the waveform. In the ZDS3000/4000 series oscilloscope, we provide a way to customize the measurement range through hardware acceleration, which can be completed in two simple steps.
Step 1: Set the measurement range to the cursor area;
Step 2: Adjust the cursor position and specify the measurement range.
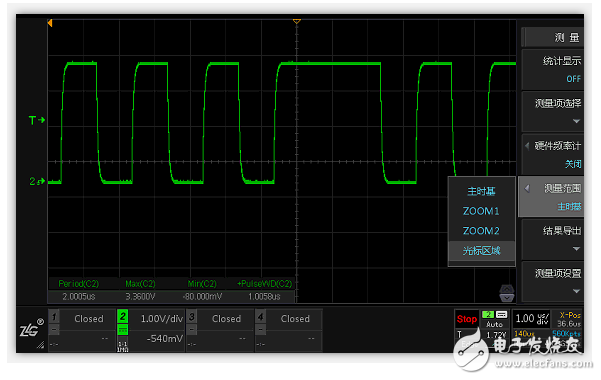
Figure 7 Custom measurement area
The measurement function is very powerful, but also very complicated. If you are not sure about the result in actual application, you can first check whether the measurement result is voltage type or time type. For voltage type, check whether the input channel setting is correct, such as probe ratio; time type is important Check whether the three thresholds, top value, and bottom value are correct.
The measurement function of the ZDS oscilloscope uses full hardware acceleration processing, which can analyze all the original (not sampled) sample points of the full screen, and perform 51 parameter measurements at the same time. The processing speed is very fast. The world’s only one with 51 types. An oscilloscope with real meaning "parameter measurement and statistical functions."
Cosmetic Bags
Specification :
1, 100% handmade, convenient ,minimalist,durable2, with strong and smooth stitching
3, Premium good nice eco-friendly PU leather
4, Any design can be made as your request
we employ the most creative designers and tech brilliant engineers to make the best cases. We believe our high-quality products with competitive prices will satisfy your needs.
The productive process :
Make the Products Mould –Cutting the fabric –Do the half products – Finish products – Cleaning –QC- Package – Shippment .
Makeup Bag,Cosmetic Bag,Makeup Bags,Cosmetic Bags
Ysure Leather case 24/7 Support : 86 13430343455 , https://www.ysurecase.com