Today, I will introduce a national invention authorized patent-electromagnetic flowmeter. The patent was applied for by Azbil Corporation, and the authorization was announced on September 7, 2018.
Content descriptionThe invention relates to an electromagnetic flowmeter for measuring the flow rate of fluids in various process systems, and more particularly to an electromagnetic flowmeter with the function of measuring the conductivity of the fluid.
Background of the inventionThe electromagnetic flowmeter is a measuring device that is provided with: an excitation coil that generates a magnetic field in a direction perpendicular to the direction of flow of the fluid flowing in the measuring tube; and a pair of electrodes arranged on the measuring tube, along with the excitation coil The generated magnetic field is arranged in an orthogonal direction, and the measuring device detects the electromotive force generated between the electrodes while alternately switching the polarity of the excitation current flowing to the excitation coil, thereby measuring the flow rate of the detected fluid flowing in the measuring tube.
Generally, electromagnetic flow meters are roughly classified into contact type and capacitive (non-contact type). The contact type is to make the electrode provided on the measuring tube directly contact the fluid of the measurement object to detect the electromotive force of the fluid. The capacitive type ( The non-contact type is to detect the electromotive force of the fluid through the electrostatic capacitance between the fluid and the electrode without contacting the electrode provided on the measuring tube with the fluid to be measured.
The capacitive electromagnetic flowmeter uses a signal amplifier circuit (such as a differential amplifier circuit) to amplify the electromotive force generated between the electrodes, and then uses an analog-to-digital conversion circuit to convert it into a digital signal, and input the digital signal to a microcontroller and other program processing devices To execute the prescribed arithmetic processing to calculate the flow rate. This kind of capacitive electromagnetic flowmeter has received particular attention from the industry in recent years because the electrodes are not easily degraded and easy to maintain.
In addition, among electromagnetic flowmeters, there are electromagnetic flowmeters that have a function of not only measuring the flow rate of a fluid but also the electrical conductivity (so-called conductivity) of the fluid. For example, Patent Document 3 discloses an electromagnetic flowmeter equipped with a two-electrode type conductivity meter. The two-electrode type conductivity meter applies an AC signal such as a sine wave or a rectangular wave between two electrodes and measures the Calculate the conductivity from the current flowing in between. The conductivity meter disclosed in this patent document measures conductivity by immersing both electrodes in the liquid to be measured.
Summary of the inventionThe inventor of the present invention conducted research on adding the function of measuring the conductivity of the fluid to the capacitive electromagnetic flowmeter. However, according to the research of the present inventors, it has been clarified that there are the following problems.
Generally, the capacitive electromagnetic flowmeter is constructed in such a way that the fluid of the measurement target does not contact the electrode, so the impedance between the fluid of the measurement target and the electrode increases. Therefore, when noise is superimposed on the line between the electrode and the input terminal of the signal amplifier circuit, there is a problem that the measurement accuracy and measurement stability of the electromagnetic flowmeter decrease. Therefore, in an ordinary capacitive electromagnetic flowmeter, the frequency of the excitation current is set to be higher than that of an ordinary contact electromagnetic flowmeter from several tens to several hundreds of Hz.
On the other hand, a conductivity meter that immerses both electrodes in the fluid (liquid) of the detection target to measure conductivity usually sets the frequency of the AC signal applied between the two electrodes to several tens of Hz to several hundreds of Hz.
Therefore, when the conventional capacitive electromagnetic flowmeter is combined with the conventional two-electrode conductivity meter, the frequency band of the excitation current required for the measurement of the flow rate and the frequency band of the AC signal required for the measurement of the conductivity There will be overlap, so the excitation current and the AC signal will interfere with each other, which may reduce the measurement accuracy and stability of the flow and conductivity.
In addition, in the conventional capacitive electromagnetic flowmeter, in addition to the above-mentioned pair of electrodes arranged in a direction orthogonal to the magnetic field, it is also necessary to contact the fluid to be measured and be connected to a common potential that serves as a reference for flow measurement. Common electrode together. Therefore, when a conductivity meter is combined with a conventional capacitive electromagnetic flowmeter, at least five electrodes are required around the measuring tube, so there is a problem that it is difficult to reduce the size of the electromagnetic flowmeter.
In particular, in the conventional electromagnetic flowmeter disclosed in Patent Document 3, since a ground ring connected to a common potential is provided between the electrode used for flow measurement and the electrode used for conductivity measurement, the electromagnetic flow The miniaturization of the design is more difficult.
The present invention is made in view of the above-mentioned problems. The purpose of the present invention is to realize a small-sized electromagnetic flowmeter with a conductivity measurement function with higher measurement accuracy and measurement stability.
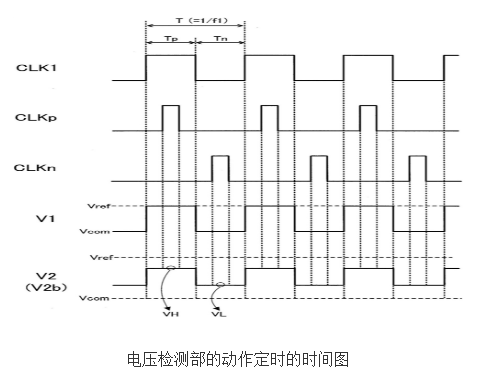
The electromagnetic flowmeter 100 of the present invention is characterized by having: a measuring tube 1, which is made of an electrically insulating material for the fluid to be measured to flow; and an excitation coil Lex, which is arranged on the outside of the measuring tube, generates communication with the supplied The magnetic field corresponding to the current Iex; the first electrode 11 and the second electrode 12, which are arranged on the outer peripheral surface of the measuring tube, are arranged oppositely in the direction perpendicular to the magnetic field generated by the excitation coil; the amplifying circuit 13, which uses a common potential Operates on the basis of Vcom, and outputs a signal VF obtained by amplifying the electromotive force generated between the first electrode and the second electrode; the flow rate calculation unit 63, which calculates the flow rate of the fluid based on the signal output from the amplifier circuit; the third electrode 2. It is formed on the outer peripheral surface of the measuring tube separately from the first electrode and the second electrode; the fourth electrode 3 is connected to the common potential and is in contact with the fluid; resistor R1, one end of which is connected to the third electrode; voltage detection Section 5, which detects the voltage of the signal generated in the third electrode by inputting an AC signal to the other end of the resistor; and a conductivity calculation section 62, which determines the voltage based on the amplitude of the voltages VH and VL detected by the voltage detection section Calculate the conductivity of the fluid.
In the above electromagnetic flowmeter, the frequency f1 of the AC signal may be at least 100 times the frequency of the AC current supplied to the excitation coil. The amplifying circuit may include filters 131 and 132 that attenuate frequency components corresponding to the AC signal included in the signal obtained by amplifying the electromotive force. It may further include a determination unit 64 that determines the presence or absence of fluid in the measurement tube based on the electrical conductivity of the fluid calculated by the electrical conductivity calculation unit.
The voltage detection unit may include: a first sample-and-hold circuit 51 that samples and holds the voltage of the third electrode during the first period Tp when the AC signal becomes the first polarity; and a second sample-and-hold circuit 52 that The voltage of the third electrode is sampled and held in the second period Tn in which the signal becomes the second polarity opposite to the first polarity. The conductivity calculation unit 62 is based on the voltage VH sampled by the first sample-and-hold circuit and the voltage VH sampled by the first sample-and-hold circuit. 2 The voltage VL sampled by the sample-and-hold circuit is used to calculate the conductivity of the fluid. The fourth electrode may be a tubular joint 3A made of metal whose one end is connected to the measurement tube and the other end can be connected to an external pipe. It may further have a shielding case 21 made of metal, and the shielding case 21 is arranged to face at least a part of the third electrode.
In addition, in the above description, as an example of the constituent elements of the invention, the reference signs in the drawings corresponding to the constituent elements are described in parentheses. According to the present invention, it is possible to realize an electromagnetic flowmeter with higher measurement accuracy and measurement stability, a smaller size, and a conductivity measurement function.
Sintered Neodymium Mangets,Ceramic Magnet,Magnet For Motor Rotor,Block Ferrite Magnet
HU NAN YUBANG MAGNETIC MATERIAL CO.,LTD , https://www.ybmagnet.com