In recent years, with the development of technology, the building of digital factories has become an important strategic goal of many companies. So how to build a digital factory has become the primary issue.
Recently, PwC Strategy& partner Yi Ping analyzed the four core characteristics of the digital factory: product intelligence, production automation, and the integration of information flow and material flow, providing a way to build a digital factory and a blueprint for success. .
Currently, building a digital factory has become an important goal of many companies, but no company has announced that it has built a fully digital factory. So, what is a digital factory? How can we build a true digital factory?
Factory digitization is not just digitization of manufacturingThe digital factory, which is often mentioned now, is only one component of "smart manufacturing." Under intelligent manufacturing, the traditional manufacturing process will be reorganized, and its ultimate goal is to realize the intelligentization of products. Among them, personalized customer needs and design, information access and sharing between suppliers and manufacturers, and quick response to after-sales services, together with digital factories, have become a very critical part of intelligent manufacturing.
The digital factory can not only cover all business links from research and development to after-sales, but can also expand to the horizontal supplier management field (see Figure "Scope of Digital Factory").
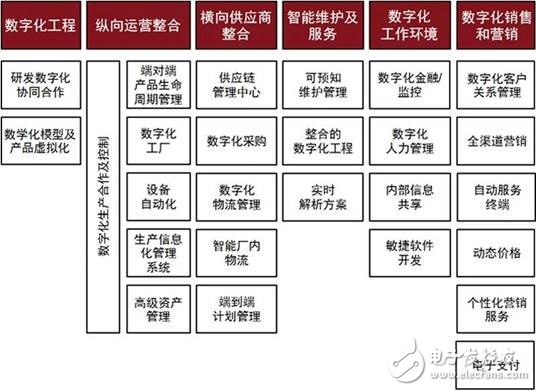
Industry 4.0 applications on the R&D engineering side include digital collaboration, digital models, and product virtualization. Through the use of information technology, R&D cycles can be greatly shortened, R&D risks are reduced, and innovation efficiency can be improved. Supply chain management mainly considers the application of Industry 4.0 from the vertical, that is, product life cycle management, and the horizontal, that is, supplier integration management. The application level is very wide, including smart factories, smart supply chains, and production information that are more familiar in China. Management systems, etc., can help companies improve the efficiency of the entire supply chain, reduce costs, and standardize the quality of upstream suppliers. Moving on to the back end, Industry 4.0 technology can also be widely used in equipment intelligent maintenance and real-time services, creating a digital working environment, and using digital technology to improve marketing efficiency and provide better sales and after-sales services.
The building of a digital factory is different from traditional business modelsDigitization can fundamentally transform manufacturing companies. The core features of the digital factory are: product intelligence, production automation, and the integration of information flow and material flow. At present, from a global perspective, no company has announced the completion of a fully digital factory. Although Siemens has model factories around the world, it has not yet fully promoted it globally. Leading manufacturing companies are adopting a series of advanced technologies to realize the digitalization of production and the entire supply chain. These technologies include big data analysis solutions, end-to-end real-time planning and interconnection, automatic control systems, digital twins, etc. With these technologies, efficiency can be improved, and companies can mass produce highly customized products. However, to fully realize the potential of digitalization, companies still need to connect with major suppliers and major customers in real time.
When discussing the future vision of the digital factory, the most mentioned is "mass customized production", which requires companies to establish relevant corporate capabilities from six dimensions:
Strong customer demand collection and analysis capabilities;
Socialized interactive product development system;
Modular and intelligent product manufacturing process;
Highly flexible supply chain management;
Production capacity (including equipment maintenance capacity) that matches customer needs;
Intelligent inventory and logistics management system.
In addition to mass-customized production, the future vision of the digital factory also includes energy saving (according to estimates, there is about 12% energy saving space), making the supply chain safer, and accurately finding solutions to problems by experts in related fields. Moreover, the production model of the digital factory is not limited to companies that produce terminal consumer products. Companies that produce equipment can also better meet customer needs, reduce costs, improve delivery efficiency, and manage production capacity by practicing digital factories.
Digital transformation made in ChinaGermany’s “Industry 4.0â€, the United States’ “Third Industrial Revolutionâ€, China’s “Manufacturing 2025â€, countries around the world have put forward a new generation of manufacturing concepts, mainly to guide the development of industrial manufacturing, in the digital, intelligent, networked In the global environment, the traditional manufacturing is promoted to upgrade to the direction of intelligent manufacturing, so as to meet the faster and more personalized demand response of the future market, and achieve lower manufacturing costs (see the "Industry 4.0 Evolution Process").
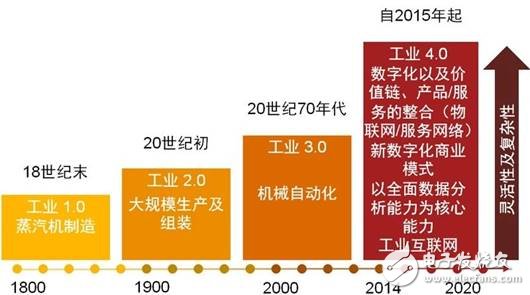
Germany’s "Industry 4.0" takes "smart manufacturing" as its development goal, and builds a "digital factory" to meet consumers' differentiated and customized needs through a series of means such as information technology, extensive interconnection, information interaction, and process reengineering. Improve production activity and provide better decision support to managers.
The "third industrial revolution" in the United States was put forward relatively early, and more emphasis was placed on the impact and influence of informatization and automation on the manufacturing industry. Of course, leading American manufacturing companies have also carried out layout and research on the intelligent trend of the manufacturing industry. For example, the Industrial Internet concept proposed by General Electric Company focuses on machine analysis, industry insight, automation and business forecasting. connect them. "Made in China 2025" was released in 2015 and became China's action plan for the first ten years of implementing the strategy of a manufacturing powerhouse. Implement five projects: manufacturing innovation center construction, intelligent manufacturing, green manufacturing, industrial strong base, and high-end equipment innovation, and carry out two special actions for quality improvement and service-oriented manufacturing. Its strategic path is driven and led by innovation, based on strong industrial base and quality improvement, focused on intelligent manufacturing, and flanked by green manufacturing and service-oriented manufacturing.
In general, the digital transformation of the manufacturing industry has just started in China. When it moves towards smart manufacturing and digital factories in the future, it is necessary to make full use of the industrial automation equipment that has been widely used by Chinese manufacturing companies.
The digital factory of the future is based on the redesigned production process, supply chain management process, product redesign, and data collection analysis and decision-making system. It needs to form a standard, and automation equipment needs to be connected to such a production system. First, it needs to have the enrichment of functions and application scenarios to meet production needs; second, to meet the needs of information collection, where the information includes products Information and operating information; third, while achieving standardized production (standardization of process technology, standardization of parts), a certain degree of production flexibility should be retained; finally, the use of automation equipment has a friendly interface, low maintenance and maintenance costs, and simple debugging, etc. Features will also accelerate the popularity of such devices.
Bosch China Digital Factory Practice-Bosch is one of the important initiators of Industry 4.0. It has leading capabilities and unique advantages in the field of Industry 4.0; it relies on the experience accumulated in the fields of mechanical design, manufacturing and software services, and has more than Extensive manufacturing knowledge accumulated by 250 factory operations has become a leader in Industry 4.0. It provides one-stop solutions including sensors, hardware devices, software and services. At the same time, more than 100 industry 4.0 pilot projects were carried out internally.
At present, the Industry 4.0 application carried out at Bosch Suzhou Automotive Electronics Factory covers many aspects. The benefits in material management, production order arrangement, equipment maintenance and personnel efficiency improvement are particularly obvious. In the production area, all workstations and raw materials are under orderly management. According to the production order, the equipment can automatically order materials, the robots can accurately locate and automatically distribute materials. Relying on big data collection and analysis to complete predictive maintenance. The shared knowledge base and visual communication system provide a strong guarantee for immediate maintenance. Realize customized reports on multiple terminals to provide employees with the most timely and reliable key data for different scenarios.
Four major challenges in transformationThe booming development of China's digital factories is gratifying, but we have also found some problems. When we contact customers who want to build a digital factory, we can usually hear them say: "We want to build a fully automated factory or'smart' factory similar to a certain company." And the next question we raise is naturally "How does your company define'intelligence'? Is there a clear digital factory strategy? Are there clear evaluation guidelines?" However, most companies do not clearly state the digital factory they want, but hope The ready-made smart factory definition can be copied directly and effortlessly. In our view, the definition of the digital factory and the evaluation indicators for success are based on multiple factors.
Challenge 1: Lack of overall strategic planning
We have observed that many projects lack holistic strategic planning, leading to unclear specific needs for future digitalization, and insufficient awareness of the current digitalization level of the company, which makes it impossible to objectively judge the gap between the two and determine the necessary reinforcement Ability.
Many Chinese companies consider the development and construction of digital factories from the perspective of software (technology) and hardware (equipment), relying on internally experienced engineers and professionals to cooperate with external suppliers to achieve specific production lines through the integration of various solutions Automation and tracking of links.
Although this move is effective, in many cases it has not solved the fundamental strategic question of "why build a digital factory". Therefore, companies should promote the construction of digital factories in a top-down manner, consider issues from the overall perspective of strategy, product design, and operational model changes, and select appropriate technologies based on their actual conditions and goals, rather than blindly Pursue the so-called cutting-edge technology. For example, Haier’s development strategy with the interconnected factory as the core not only conforms to the group's development direction of mass customization, but also fits Haier's rich experience in modularization and digitalization, thus successfully creating an ecosystem of interconnected factories.
Challenge 2: Can't get out of the narrow misunderstanding of benefit
In some specific industries, especially in the field of discrete manufacturing, the degree of digitization and automation depends on the current infrastructure, the products produced and the entire production process. To achieve a high degree of digitization or automation, it may take a long time for the accumulation of technology to be feasible. From the perspective of cost-effectiveness, it will take a long time to recover the investment. Therefore, if you consider the issue of benefits purely from the perspective of return on investment, companies will hesitate when facing the digital factory. Today, when sustainable development is increasingly valued, production safety is continuously regulated, and labor dividends are gradually disappearing, the energy saving and emission reduction, human-computer interaction, and remote control achieved by digital factories closely follow the requirements of the current situation and can bring significant social benefit.
Companies can use some quantitative indicators, such as production efficiency, single-person output, energy consumption, quality control (defective product rate), production cycle, etc., to evaluate the benefits of digital factories. Qualitative indicators such as reducing manual work, improving employee morale (work is no longer boring, but more interesting, with higher added value) and increasing employee loyalty can also be used to assist evaluation. The different demands of the industry and the enterprise itself will also have a certain impact on the choice of indicators. In addition to common indicators such as production efficiency, yield, and production cycle, a leading textile company also chose to change production time and use the number of workers to measure the effectiveness of its digital factory, while a construction machinery giant added production to its demonstration workshop. Misoperation, logistics efficiency and other indicators solve its own pain points.
Challenge three: Failing to fully consider the technology
The development time of automation and digitalization in China's manufacturing industry is relatively short. Even in the same industry, the degree of automation and technical routes of enterprises are quite different. The data distribution is relatively scattered, it is difficult to obtain the systematic data of the product life cycle required by the digital factory, and it also makes the formulation of standards difficult. In some of the more traditional industries, Chinese companies are scrambling to plan to achieve leapfrog development of digital factories. However, the backward equipment in the factory floor makes it difficult to capture and transmit data in real time, which is a major problem that Chinese companies have to face. Nevertheless, there are still solutions represented by Andon systems that can supplement manual operations and are effectively integrated into factory automation.
At the same time, Chinese companies often pay more attention to the automation rate of individual equipment, ignoring that the production system is an organic whole, and in different systems such as enterprise resource planning (ERP), manufacturing execution system (MES), and product life cycle management (PLM) There is also room for improvement in connection and integration, and it is even rarer to achieve interconnection between different factories. Therefore, companies need to formulate a technology roadmap based on their own digital factory strategy, and implement various technological transformation measures in stages, so as to minimize the risks of implementation and avoid impacts on business and operations.
Challenge 4: Talent is still the bottleneck
Digitization and automation will undoubtedly reduce manual repetitive tasks, improve the working environment, and protect personal safety. We believe that the manufacturing industry can seize this opportunity to change the traditional image of "poor working environment" and attract more new talents through upgrading. The digital factory highly integrates the production and operation process, which puts forward higher requirements for technical talents. In the past, professionals in a single field will no longer be applicable, and will be replaced by multi-fields, stronger learning capabilities, and digital delivery. Compound talents.
With reference to advanced foreign experience, the vocational education system that combines classroom education and practical work has pointed the way for the development of digital factory training projects for industry-university cooperation. For example, a leading machine tool company directly established a joint college with a local engineering college, through the integration of production and education and complementary resources, to train and transport talents for the construction of its digital factory. In addition to the educational mechanism, vocational training courses themselves need to be adjusted to achieve standardization of course training, and to increase talent training in traditional fields such as business, natural sciences, and engineering, and cultivate proficiency in data analysis, product management, project management, Interdisciplinary digital engineer in IT architecture or information security.
Finally, because the transformation of a digital factory requires multi-department coordination, it often requires top-level decision makers to have a strong determination and a deep understanding of digitalization, which can guide the entire enterprise to formulate a digital strategy, lead the company through the transformation smoothly, and create a successful digitalization factory.
Blueprint for digital transformation of Chinese factoriesLeading industrial companies have taken solid steps in the construction and development of digital factories. While improving production efficiency, they can quickly and reliably produce more customized and high-quality products to serve the market. For many companies that have no plans to build a digital factory, the lack of a digital vision and corporate culture is the biggest obstacle that keeps them from moving forward. In our opinion, this is a major element that is not available to the pioneers of the digital factory.
The digital vision not only considers various technologies, but also defines how these technologies work together throughout the product life cycle and the corporate ecosystem. Other factors that hinder companies from developing digital factory plans include uncertain opportunities, unclear economic benefits, and high investment costs. Taking these factors into consideration, companies need not only a clear vision, but also a practical digital roadmap. PwC Strategy& has developed a six-step blueprint to assist companies in formulating or optimizing a roadmap to successfully cope with the challenges on the road to the digital factory and Industry 4.0 (see Figure "Digital Factory Success Blueprint" ).
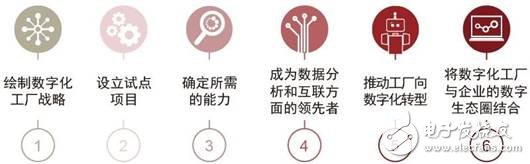
Developing a coherent strategy is absolutely the top priority. The digital factory involves the adoption of different technologies, and many technologies are easy to rush into operation temporarily. Companies need to have clear ideas on how to match the overall strategy and operational goals of various technologies, and how to cooperate with other existing technologies, and the digital vision should also cover the entire organization, allowing the digital factory to play a 1+1"2 role. Before formulating a digital factory strategy, companies need to recognize their current maturity, ensure that talents and technology are given equal attention, and focus on projects that can maximize value. Finally, it is necessary to form a supporter team composed of high-level, middle-level and workshop workers to jointly promote the implementation of the strategy.
Set up a pilot project
The economic benefits of digitalization are sometimes not easy to quantify, and at the initial stage, the team can only provide very limited technical concepts and demonstrations, which may make it difficult to obtain funding and the approval of stakeholders.
The means to solve these problems is to experiment. Through pilot projects, companies can find the most suitable way for themselves, show the quick-win results to the entire organization and gain their approval, and then obtain funds for large-scale promotion. Since the digital factory may bring far-reaching changes to the entire workforce, workers need to be included in the pilot work.
Vertical integration of one or two production bases from digital engineering design to production planning supported by real-time data is a feasible pilot program. Installing sensors and actuators on major production equipment, or using data analysis to explore predictive maintenance programs can also achieve initial results. It is also possible to realize the digitization of a specific product line in a specific factory and use it as an opportunity for continuous learning and optimization. Of course, companies can also consider cooperating with external digital leaders such as start-ups, universities or industry organizations to accelerate the pace of digital innovation.
Determine required capabilities
What is most important in the production process? Better and more automated logistics? Provide workers with timely, customized information? Sensor integrated network? We believe that considering this issue from the perspective of capabilities can bring greater value. The goal of the digital factory is not to implement the coolest new devices, but to achieve specific goals such as improving efficiency, improving quality, or enhancing the business itself. Based on the experience gained in the pilot, from the four strategic dimensions of organization, talent, process, and technology, combined with the company's production strategy and overall business goals, it should outline in detail the capabilities of the digital factory and the structure of the factory system.
Become a leader in data analysis and interconnection
Process and quality improvement, resource management, preventive maintenance, in the digital factory, these solutions are almost always closely related to interconnection. Sensors help collect data, analyze it at the information level, and then transmit it back to networked logistics facilities and production equipment to adjust production in real time. Every company needs to be proficient in interconnected tools and systems that can generate and transmit data, as well as analytical tools to improve efficiency and quality.
Promote the digital transformation of the factory
The road to the digital factory is a road of transformation. As with other transformations, managing change and its impact on employees is the key to success. Difficulty in finding qualified talents, lack of a digital corporate culture, and some employees' reluctance to embrace digital changes are common challenges. The solution to these problems is to work with employees as early as possible to invest in training and continuing education, and these investments will be offset by the efficiency improvements brought by the digital factory. The cultivation of the digital environment must have the full support of the leadership. The senior management must regard the digital factory strategy as the focus of their work, abandon the conservatism and speed up the project approval process, so that the digital team can accelerate the transformation process. At the same time, it is also necessary to design a concise reporting channel to ensure that the digital team focuses on various value-added activities rather than dealing with various administrative requirements.
Combine the digital factory with the corporate digital ecosystem
In the process of promoting the digital factory, many companies are focusing on the vertical integration within each factory. The realization of the connection between the MES system and the ERP system within the factory can indeed achieve significant improvements. But as part of the digital ecosystem, the digital factory should play a greater role. When companies horizontally integrate supplier and customer information along the entire supply chain with digital factories, it will bring greater efficiency improvements. Just imagine: you can use real-time short-term customer needs to adjust planning and production conditions, flexibly make adjustments according to customer requirements, and obtain maximum customer satisfaction at the lowest cost. This vertical and horizontal integration strategy using tracking technology not only allows companies to optimize planning processes and production execution, but also deepens the bonds between companies and strategic suppliers and customers.
However, these tasks are only the beginning. If companies can integrate digital functions in their products, it is possible to create a series of services to transform abstract data into concrete value. The production process itself can also convert the collected data into income through a variety of ways. Under the far-reaching influence of the digital factory, companies can expand or even completely change the current business model, not only focusing on production links, but also having the opportunity to expand their share in the lucrative after-sales market, increase profit margins, and enter new businesses field.
External Rotor Motor,Outer Rotor Motor,External Rotor,External Rotor Fan
Wentelon Micro-Motor Co.,Ltd. , https://www.wentelon.com