Abstract: MSM6882 is a data modem produced by OKI Corporation of Japan using the minimum frequency shift keying method. The device contains receive, transmit, and clock generation circuitry, and the data transfer baud rate is selectable between 1200 bps and 2400 bps. The main performance and working principle of MSM6882 are introduced in this paper. The application circuit design of MSM6882 in wireless communication is given.
1 Introduction
The popularity of computers and data terminals has made wireless data communication technology widely used in many fields. In wireless data transmission equipment, the modem is an indispensable part. The modulation methods of the modem mainly include frequency shift keying (FSK) and relative phase shift keying (DPSK). Among them, the minimum frequency shift keying (MSK) modulation method is a better one of the FSK methods. The MSK modulation method is a special case of the continuous phase frequency keying (CP-FSK) method, and its modulation coefficient is 0.5. The MSK signal has no phase abrupt change at the symbol conversion instant, so the roll-off of the signal spectrum outside the frequency band is accelerated, and the occupied frequency band is narrower than the PSK signal, but has the same performance as the PSK, and is very suitable for use in wireless communication.
The MSM6882 is a modem chip manufactured by OKI Corporation of Japan using MSK modulation. It operates from -25°C to 70°C and is available in DIP22 or SOC24 packages. The main features are as follows:
â— The on-chip filter adopts a switched capacitor structure; 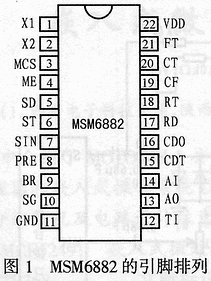
â— Data transmission baud rate 1200/2400bps optional;
â— The on-chip transmit filter can be used as an audio signal filter alone;
â— Receive timing regeneration circuit has two synchronization modes for the user to select;
â— An oscillating circuit is integrated in the chip;
â— Modulation can adopt sine or cosine mode;
â—Powered by a single 5V power supply (MSM6882-5).
2 MSM6882 pin function
The pinout of the MSM6882 is shown in Figure 1. The pin functions are described as follows:
X1, X2: Crystal input pin. When an external clock is connected, X1 is left floating.
MCS: Clock frequency selection terminal. When the pin is "0", the external crystal or clock is selected as 3.6864MHz. When it is "1", the external crystal or clock is selected to be 7.3728MHz.
ME: Modulator enable. When the terminal is "0", the TI pin is connected to the transmitting low-pass filter. When it is "1", the modulator is connected to the transmitting low-pass filter.
SD: Send data input pin.
ST: Transmit clock output pin. The signal of the SD pin can be synchronized with the rising edge of the ST signal during use.
SIN: Sinusoidal modulation mode selection.
PRE: Send data preset selection. When it is "0", the SD pin signal is output to the AO pin.
BR: Baud rate selection bit. The selection method is listed in Table 1.
Table 1 baud rate selection table
| Clock frequency (MHz) | MCS | BR | Baud rate (bps) |
| 7.3728 | 1 | 1 | 2400 |
| 1 | 0 | 1200 | |
| 3.6864 | 0 | 0 | 1200 |
SG: On-chip analog signal ground.
GND: Chip power ground.
TI: Audio signal input.
AO: Modulated signal output.
AI: Demodulation signal input.
CDT, CDO: Chip test foot. In normal use, the CDT pin should be grounded and the CDO foot should be left floating. 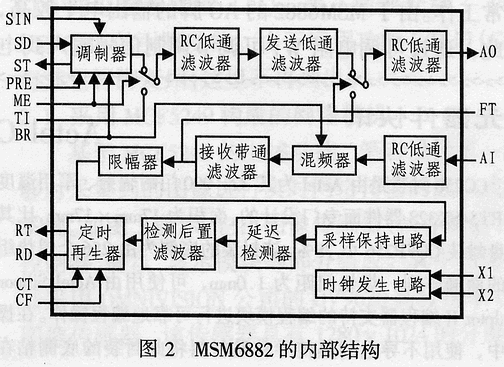
RD: Receive data terminal. The demodulated signal is serially output from this pin.
RT: Receive data clock. The RD pin data can be synchronized with the falling edge of the RT signal during use.
CF: Fast phase lock control. When the terminal is "1", the phase difference between the output signals of the RD pin and the RT pin is greater than 22.5°, and the phase correction will be completed quickly; if the phase difference is less than 22.5°, the phase correction is performed at a low speed. When the pin is "0", the phase correction is performed at a low speed regardless of the phase difference of the output signals of the RD pin and the RT pin. Normally, the pin is connected to a high level, that is, the fast phase locking mode is selected.
CT: Synchronous mode selection. When "0", the phase locked loop completes phase synchronization within 50 bits. When it is "1", the phase-locked loop completes phase synchronization within 18 bits.
FT: Self-loop test control. Usually connected to a high level.
VDD: Chip power port.
3 MSM6882 internal structure principle
The internal structure of the MSM6882 is shown in Figure 2. The circuit is mainly composed of three parts: a transmitting circuit, a receiving circuit, and a clock generating circuit. The transmitting circuit includes a modulator, a transmit low pass filter, and two RC low pass filters. It can perform modulation of the input binary data or filtering of the input audio signal under the control of the PRE and SIN input signals. When the modulation function is completed, the input data is first modulated by the modulator into an MSK signal, and the high-frequency components are filtered by the transmission filter and the two RC low-pass filters and smoothed, and then output to the line. When the audio filtering function is completed, the transmit filter will be disconnected from the modulator and connected to the TI terminal to directly filter the incoming audio signal and send it to the line.
The receiving circuit is composed of an RC low pass filter, a mixer, a receive band pass filter, a limiter, a sample and hold circuit, a delay detector, a detection post filter, and a timing regenerator. After the received signal is filtered by the receiving filter, it can be converted into a square wave signal input delay detector by the limiter and the sample and hold circuit. The demodulated data is then recovered by the delay detector, sent to the timing regeneration circuit via the detection filter to extract the reception clock, and finally the reception clock and the demodulated data are output.
image 3
The clock generation circuit provides timing signals for the entire circuit.
4 application circuit
Figure 3 shows the actual application circuit of the MSM6882. The communication baud rate of this circuit is 1200 bps. Since the MSM6882 sends and receives data to synchronize with the synchronous clock, the 82C51 asynchronous serial communication interface chip should be selected to connect the MSM6882 to the AT89S52 microprocessor. The PTT of the radio can be controlled by the RTS pin of the AT82C51, while the RTS controls the transmit enable of the MSM6882 by the inverted signal. The SPK pin and MIC pin of the radio are connected to the AI ​​pin and AO pin of the MSM6882 through their respective coupling loops. At the time of design, the input clock period of the CLK pin of the 82C51 microcontroller should be in the range of 0.42μs to 1.35μs, otherwise the chip may not work properly. Since the output level of the AO pin of the MSM6882 is high, the amplitude of the modulation signal input to the station can be adjusted by the adjustable resistor W1. The SPK signal from the radio interface is sent to the AI ​​pin of the MSM6882 after being limited by the signal, and the other is amplified, detected, and amplitude-amplified and sent to the DSR pin of the 82C51 as a carrier detection signal. At the same time, the sensitivity of the carrier detection signal is adjusted by W2. When the system detects the signal, it can adopt delayed transmission to avoid co-channel interference and channel congestion. For the operation method of the 82C51, refer to related books, which will not be repeated here. For the occasions with high anti-interference requirements, the radio signal can be isolated between the radio and the modem by adding a transmission line transformer. Due to space limitations, it will not be repeated here.
Power X (Qingdao) Energy Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.qdpowerxsolar.com