[Home Theater Network HDAV.com.cn] Speaker divider can divide the sound signal into several frequency bands. For example, the divide-by-2 is composed of a high-pass filter and a low-pass filter.
A three-way frequency band adds another bandpass filter. The crossover is the "brain" in the speaker, which is very important for the sound quality.

Problems with the use of the frequency divider The audio technology frequency divider is an audio device that can divide the sound signal into several frequency bands.
We know that the frequency range of the sound is between 20Hz and 20kHz. It is hoped that using only one speaker will ensure that a wide frequency sound such as 20Hz-20kHz is difficult to achieve, because this will be technically different. A variety of problems and difficulties. Therefore, under normal circumstances, in order to ensure the frequency response and the frequency bandwidth of the reproduced sound, in the professional range, the high-bass split speaker is mostly used for sound reproduction, and when the high-bass split type speaker is used for sound transmission, It is necessary to use a frequency divider.
structure
The speaker crossover adopts the structure of the following figure, and the specific analysis:
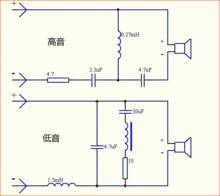
The circuit that connects the tweeter: let the current flow through the capacitor first, block the low frequency, let the high frequency pass, and the horn is connected in parallel with a coil to make the coil generate a negative voltage. This voltage is exactly a voltage compensation for the tweeter, so it can The sound current is reduced approximately realistically.
Connect the woofer circuit: the current flows through the coil first, so that the high frequency part is blocked, and the low frequency band passes smoothly because the coil is basically not obstructed. Similarly, the woofer is connected in parallel with a capacitor, which is to use a capacitor to generate a high frequency. The voltage is used to compensate for the lost voltage, which is the same as the tweeter.
It can be seen that the characteristics of the capacitor and the coil that are fully utilized by the frequency divider are divided. However, the coil and the capacitor still consume the voltage in the respective blocked frequency bands, so the circuit divider will lose a certain sound, and there are many compensation measures. Because the author has insufficient knowledge, it is difficult to say clearly. The electronic crossover solves this problem. When the sound is input to the power amplifier, the frequency is divided first, and then a special amplifier circuit is used to amplify the different frequency bands, so that the sound distortion is small and the reproduction is realistic. But the circuit is complicated and expensive.
effect
1. Make all kinds of speakers work in the most suitable audio segment
Speakers with different diaphragm sizes and materials have different operating bands. The louder the speaker, the better the low frequency characteristics. Therefore, under the same conditions, the 18-inch bass effect is definitely better than the 15-inch bass effect.
The better the rigidity and brittleness of the diaphragm material, the lighter the quality, and the better the high frequency characteristics of the sound reproduction. Many tweeters use titanium film or indium film as the diaphragm material to improve their high-frequency characteristics. The diaphragm of the woofer generally uses materials such as paper, carbon fiber, bulletproof cloth and rubber (edge) to facilitate bass reproduction.
The frequency divider can be used to send high-frequency signals to the tweeters, and the low-frequency signals are sent to the woofer. The high- and low-frequency signals are used in different ways, and the operating band advantages of the respective speakers are utilized as much as possible to ensure the speakers in different working frequency bands. Give full play to make the playback characteristics of each frequency more balanced.
2. Cutting distortion caused by different vibration amplitudes of different frequency sound speaker diaphragms
When the speaker is pronounced, its vibrating bass vibration amplitude is large and the high-pitched vibration amplitude is small. Theoretically speaking, the vibration amplitude of the speaker cone is inversely proportional to the square of the reproduction sound frequency, that is, the same speaker diaphragm, the lower the frequency, the larger the amplitude under the action of the signal voltage of the same amplitude, that is, if the frequency is increased 10 times, the amplitude will be reduced by a factor of 10, or 100 times.
If we use a single speaker to produce a wide range of frequencies, it is very difficult to have a very wide amplitude of vibration due to the mechanical properties of the diaphragm. This will inevitably cause distortion of the sound and make the sound quality reproducible. Affected.
The study found that the cutting distortion has the greatest influence on the bass. When the woofer delivers the bass, as long as there is a high-pitched component, it will inevitably lead to cutting distortion, causing the bass to tremble and tremble. Of course, the distortion of the tweeter will also make the treble hoarse, but it will not affect the bass.
3. Reduce the sound produced between different speakers in the same speaker
Interference phenomenon For the tweeters and woofers in high and low-pitched speakers, although they work in different frequency bands, if the full-range signal is sent to the tweeter and woofer without dividing the frequency, it will definitely appear high. When the woofer emits the same sound at the same time, when the same sound of different speakers meets, it is very likely that people who have mutual interference with sound waves have a little common sense. Once the sound interference occurs, the comb filtering effect appears. A series of problems, such as waves, which affect the sound reproduction in varying degrees.
After setting the frequency dividing circuit, the treble and woofer respectively obtain their own best working frequency sound signals, and the frequency range of sounds between them is hardly covered, except for a small amount of interference in the speaker crossover point and the crossover cross area. The interference of frequency sounds no longer exists.
The reason why the frequency interference phenomenon exists in the crossover point and the crossover crossover area is very simple, because the frequency division attenuation rate of the frequency divider cannot be made infinite, in the crossover intersection area, especially at the crossover point, the tweeter and the bass. The speaker will have the sound of the other band at the same time, and the phenomenon of sound interference is inevitable. Therefore, the higher the frequency division attenuation rate of the frequency divider, the smaller the frequency division intersection area, and the smaller the sound interference of the speaker.
Characteristics
There are two main types of frequency dividers: one is the passive crossover (PassiVe Crossover), also known as the power divider; the other is the active crossover (Active Crossover), also known as the electronic crossover.
1, passive crossover

The passive crossover is a built-in frequency divider for the speaker. It consists of a capacitor and an inductive filtering network. It is characterized by a crossover network placed between the power amplifier and the speaker. This crossover divides the full-range audio power signal directly from the power amplifier into bass and treble or bass, midrange and treble, and distributes the divided signals to the speakers of each band in different frequency bands. In the full-frequency high, low or high, medium and low-frequency active crossover speakers, the frequency division task is completed by the passive frequency division circuit.
The advantages of passive crossover are: firstly, the structure is simple, the cost is low, and it is installed with the sound, it needs to be adjusted and is easy to use. Secondly, it is easier to connect the system. Just input the full-frequency signal to the power amplifier and connect the amplifier to the speaker. Together, full-range playback can be achieved. Third, there is less power amplifier required. Generally, one power amplifier can carry two full-frequency passive crossover speakers, so the system cost is low.
The disadvantage is that the crossover network has to bear a lot of power and current applied to the speaker, so a larger volume of inductance is used, and since the inductance parameter is directly related to the speaker impedance, the impedance of the speaker is a function of frequency. Deviation from the nominal value is large, so the error is large, and the calculation is difficult. Secondly, after the power audio signal output by the power amplifier passes through the capacitor and the inductive filter, the distortion of the capacitance and the inductance is inevitable, and the sound is distorted. Thirdly, the audio power signal output from the power amplifier will cause loss of power signal after each capacitor and inductor device, so the power signal loss of passive frequency division is large; finally, the frequency division attenuation rate cannot be made too high. Generally, the maximum 12dB/octave is too large, and the interference in the crossover crossover area is too large. This is because the way to improve the frequency division attenuation rate of the passive frequency divider is to increase the capacitor or inductor, that is, the filter order, but increase the capacitor or inductor. The number of devices means that the signal distortion and power loss increase, and the result of increasing the frequency division attenuation rate brings more
As the name implies, passive frequency division is a kind of “frustrationâ€: the frequency division method, the full-frequency power signal output by the power amplifier has to be divided, and the frequency division will lead to a series of problems, so it can only be forced to divide the power signal. . In order to reduce system cost, civil speakers all adopt passive frequency division. Professional speakers are very different from those of civilian speakers in terms of requirements, listening subjects and users. In addition to passive crossover speakers, there are also active crossover speakers.
2. Active crossover

The active frequency divider is a device that divides the full-frequency audio weak signal, and is generally composed of an active electronic circuit frequency division system. The frequency division system is located in front of the power amplifier, and the full-frequency audio is weakly divided. The bass, treble or bass, midrange, and treble signals are sent to their respective power amplifiers, and then output by the power amplifier to the bass, treble or bass, midrange, and tweeters. This method is called active crossover. In the case of weak signals, the frequency division can be achieved with a low-power electronic active filter.
Each speaker unit of the passive crossover speaker has its own power signal interface. Some high- and low-bass discrete speakers can have active crossover and passive crossover. These speakers are equipped with active crossover. (Active) and passive crossover (Passive) switch, the switch on some speakers is also equipped with a locking mechanism to avoid false triggering. When adopting the active crossover mode, be sure to turn the crossover mode switch to the "Active" side, and connect the high-pitched power amplifier to the high-pitched (Hi2h) input and the bass power amplifier to the low-speed input.
The advantages of active frequency division are many. First, due to the use of weak signal electronic line signals for frequency division processing, the sound signal loss is small, the distortion is small, and the reproduction sound quality is good. Second, the frequency division attenuation rate can be made higher than the passive frequency division. It is easy to reach 24dB/octave, the crossover crossover area is much smaller than the passive crossover, and the interference between the high and low volume sounds in the crossover crossover area is basically overcome; the third is good adjustability, electricity The sound index is high.
None of the shortcomings of active crossover is related to sound quality. The main problems are: First, high cost and large investment. Since the active crossover mode is high and the bass is used separately with separate power amplifiers, there are many power amplifiers, such as one-to-two distributed speakers to be driven by two amplifiers; the second is to add an electronic crossover, which makes Connection and adjustment aspects increase the difficulty of use.
Instructions
As mentioned above, the frequency divider has two types: active frequency division and passive frequency division. The passive crossover is fixed inside the speaker and does not need to be adjusted by the sound engineer. The active crossover method has many problems such as the correct use of the electronic crossover, reasonable connection and adjustment, so this article only Several major issues that should be noted in the use of active crossovers are discussed.

(1) Panel and function keys
The function of each function key, button and interface is described below.
Input gain. The input signal level is adjusted, usually placed at the rib B position.
(2) LF
Bass delay. O-2ms (maximum 60cm) delay for the bass.
(3) LF/HF GAIN
Low frequency / high frequency gain. Adjust the level of the low frequency band and the high frequency band.
(4) MUTE
Mute. Block the signal of a certain frequency band.
(5)x-0VER PREQ
The crossover frequency (divide point), when divided by two, there is only one crossover point; when three is divided, there are two crossover points.
(6) RANGE
Frequency range—The frequency range is selected between 90-900 Hz or 900 Hz-9 kHz.
(7)MODE
Divided mode, two-channel two-way or mono three-way selection.
(8) MONO BASS
Mono bass, in mono stereo mode, you can select a mono bass output.
(9) CD EQ
Constant pointing horn equalization, in the case of using a constant pointing horn (US EV company patent), can make the high frequency band characteristics better.
(10)LIMITER
Limit button. Output signal gain limit adjustment, used to limit excessive signal and protect the amplifier speaker.
(11)THRESHOLD
Threshold selection key. Choose a limit threshold range with -6dB and +18dBu options.
The back panel of the electronic crossover is generally based on various interfaces, as shown in Figure 2. The functions of each interface and function keys are described below.
(12) FUSE
Insurance and power outlets..
(13)SERIAL NUMBER
Product serial number.
(14)HIGH/MID/LOW OUTPUT
High frequency / intermediate frequency / low frequency output interface. When the two-channel two-way output is output, the high-frequency and low-frequency are output according to the frequency band above the interface; when the channel is three-way, the high-frequency, intermediate-frequency and low-frequency are output according to the frequency band below the interface.
(15)POLARITY
Polarity (phase) button, which can be used for inverting adjustment.
(16) INPUT
Signal input interface. The full-range signal is input from this interface, and the signal is input from the left channel when the mono three-way mode is used.
More fresh and fun home theater information, please pay attention to home theater network http:// (WeChat: cnhifi), the country's most influential home theater audio player interactive media website.
Linear Actuators,Column Lift Linear Actuator,Motorized Linear Actuator,High Speed Linear Actuator
Kunshan Zeitech Mechanical & Electrical Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.zeithe.com