0 Preface
There is a great expectation that white light-emitting diodes (LEDs) will be used for general illumination. This further promotes the replacement of LEDs as fluorescent lamps for general lighting, and the improvement of the efficiency of LED components, and the energy conservation of Led Lighting dimming control, thereby striving for high efficiency and miniaturization.
In order to solve this problem, Toshiba Lighting Technology Co., Ltd. (TLT) has developed led lighting power supplies to meet the performance and functional requirements of LED lighting equipment, such as low power consumption, high efficiency, and compact structure. A high-efficiency buck-boost converter for controlling the current of the LED. In the dimming control, it is divided into amplitude control and pulse width modulation (PWM) according to its use. In PWM with brightness change but color temperature is not easy to change, frequency illumination is much higher than the camera image frequency, and thus, in the image The flicker that occurs in the image can be suppressed.
TLT is also committed to the development of LED lighting equipment that utilizes natural energy sources, such as wind-solar complementary lighting systems consisting of solar photovoltaic power generation, wind power generation and batteries.
As a new light source in the 21st century, white LED has a lot of room for future development. Nowadays, fluorescent lamps widely used as general illumination, in order to promote their replacement, require LED lamps to have the same or higher functions and performances than current lighting fixtures, and have a greater expectation for energy saving. In addition, the dimming control functions necessary for today's lighting fixtures, as well as some functions that effectively play the four-D features in LED lighting, are of course indispensable.
In order to meet this important demand, TLT has developed the power supply and dimming control technology for LED lighting. The author has integrated lighting power and dimming control technology for LED characteristics, and also used natural energy for LEDs in recent years. The off-grid power system for lighting is introduced in turn.
1 LED lighting power supply
When considering the dimming control of LEDs, it is important to fully grasp the characteristics of the LEDs. Its main features are as follows: (1) The component unit is operated by a low voltage DC; (2) In the case of modularization of most components, the degree of freedom of voltage and current is selected; (3) The voltage and current characteristics are The exponential function characteristic curve has a characteristic curve at different temperatures; (4) The operating voltage of the component may fluctuate.
The forward voltage (Vf) and forward current (If) curves of the LED are temperature-dependent, characteristic curves that vary according to an exponential function (Figure 1). Since the manufacturing error also includes the difference between the components, it is necessary for the power supply circuit to have a current control function that maintains a stable operating point.
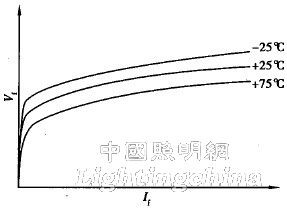
Figure 1 Temperature-dependent Vf-If characteristic curve
Figure 2 shows the circuit structure combined with a current-control function and a buck converter that improves circuit efficiency. In order to keep the current flowing through the LED constant, the 4 is fed back through the PWM integrated circuit to control the duty ratio of the switching element, that is, to control the ratio of the on and off in one cycle.
In order to suppress higher harmonics in the input current, as in the case of the discharge lamp, a step-up chopper circuit is inserted in the front stage of the constant current circuit in accordance with Japanese Industrial Standard 1ISC 61000-3-2.

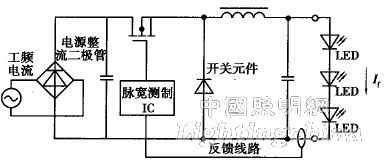
Figure 2 LED lighting with buck converter circuit
2 dimming control
LED dimming methods include amplitude control and pulse width modulation. In the amplitude control, the brightness is adjusted by controlling the DC current value of the LED; in the pulse width modulation, the current of the LED is turned on/off at a certain frequency, and the brightness is adjusted by controlling the ratio of the on-time. . The advantage of pulse width modulation is that although the brightness changes but the color temperature is not easy to change; the disadvantage is that it is not suitable for general illumination dimming due to flicker (Fig. 3). Hereinafter, the respective control methods will be described.
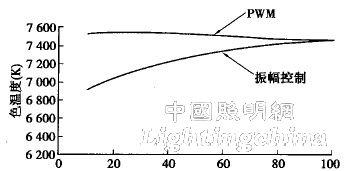
Figure 3 color temperature and dimming control
2.1 Amplitude control
Amplitude control is a dimming control method for general illumination. Pulse width modulation is sometimes not suitable for combination with an illuminance sensor (the illuminance sensor is used to control the constant brightness). The dimming means in the amplitude control mode are roughly divided into two types: a form separate from the power supply, an external dimming signal input (4-wire type), and an input phase control power supply waveform (2-wire type). Each form must have its own circuit technology.
2.1.1 4-wire
This is a form of dimmer for fluorescent lamps that is widely used in general lighting, and is also a method for controlling downlight and base light of LEDs. The circuit structure is shown in Figure 4.
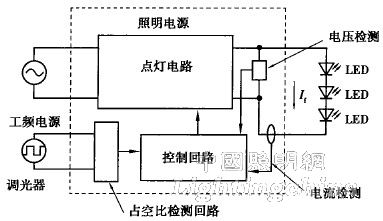
Figure 4 4-line amplitude control dimming
Corresponding to the dimming signal from the dimmer, the brightness is adjusted by changing the target value of the LED current. However, the problem is that when the dimming lower limit is close to 0 for deep dimming, the current value is difficult to detect. In the Vf-If characteristic of the LED shown in FIG. 5, the low current region surrounded by the broken line has no feedback of current, and only the LED voltage feedback is used to control the brightness. With this smooth transition of current and voltage feedback, it is possible to perform deep dimming by amplitude control.