Case scenario
The SCADA system in the Drainage Group's online business area needs to collect data from the I/O Server in the DMZ area. The SCADA system can use some IPs to collect data from the I/O Server normally, but another part of the IP cannot be normal from the I/O. Data is collected on the server, indicating an exception and disconnecting.
For example: 10.2.103.8 is the IP address of the SCADA system. It can collect data from the I/O Server of 10.2.0.51 and 10.2.0.52 normally, but the IP of the SCADA system is changed to: 10.2.103.10, which cannot be normal from 10.2. Data is collected on the I/O Servers of .0.51 and 10.2.0.52.
case study
Network topology diagram (simplified)
The following figure shows a simplified topology diagram. We show the communication link between the SCADA system and the I/O Server. The port mirroring is used to bypass the deployment of the network to the SCADA system and the I/O Server. The analysis system collects communication packets between the SCADA system and the I/O Server.
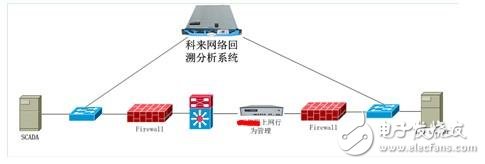
Figure 1 network topology
Troubleshooting
We collect communication data from the interactive machine in the DMZ area and the interactive machine on the online business area, and carry out comparative analysis to see what causes the failure of the business system.
DMZ zone switch data
In the DMZ zone switch data, you can see that a large number of RST (reset) packets are sent to 10.2.0.52 in the TCP session, as shown in Figure 2. These connections are released by these reset packets, but why are there so many reset packets? Who sent these packets?
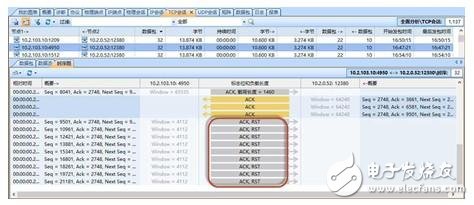
Figure 2 TCP session captured in the DMZ area
By looking at the transaction timing diagram of the Kelai network backtracking analysis system, it can be found that the TTL (time to live) value of the reset packet is 127. When the data is transmitted normally, the TTL (time to live) value is 61, and when it is abnormal. Obviously different, the reset packet is not sent from 10.2.103.10, but an intermediate device sends a reset packet to interrupt the normal application session.
The advantage of USB Cable Type C is that it supports higher current, that is that more current can be passed by Type-C in the same time. In this way, the charging speed of the device can be accelerated. At present, the charging current of most Type-C data lines is generally 2A. If the charging rate of 3A is to be reached, a high-current wall charging matching it is required. That is to say, if the wall charge only supports 1A, whether it is charged with 2A or 3A data line, there is no difference fundamentally. If the current supported by the wall charging is 2A, and the type-C data cable of 2A/3A is matched, the effect can be significantly changed.
In addition, the device equipped with the Type-C interface can be charged by connecting the mobile power supply through the Type-C cable or Usb C Cable. Users do not need to carry the charging cable, but can have the wall charging and Type-C cable. In addition, when selecting a Type-C charging cable, We should pay attention to the current limit. The charging data cable 1A does not have fast charging performance, 2A is the most commonly used Type-C charging data line, and 3A is the best data line at present. If you want to have fast charging effect, you must choose the Type-C charging data line with 3A current.
The highlights of Type-C interface are thinner design, faster transmission speed (USB3.1 up to 10Gbps) and stronger power transmission (up to 100W).The biggest feature of Type-C double-sided plugable interface is that it supports double-sided insertion of USBinterface. Officially solved the USB never insert the worldwide problem, the front and the back of the random plug.The USB Cable used with it must also be thinner and lighter.

Usb Cable Type C,Usb Type C Cable,Type C 3.0 Cable,Usb Type C Data Cable
Henan Yijiao Trading Co., Ltd , https://www.yijiaousb.com