1, main memory overview
(1) Two important technical indicators of main memory
â—Ž read and write speed: often measured by the storage period, which is the time interval necessary to continuously initiate two independent memory operations (such as read operations).
â—Ž Storage capacity: Usually measured by the number of bytes or words constituting the memory.
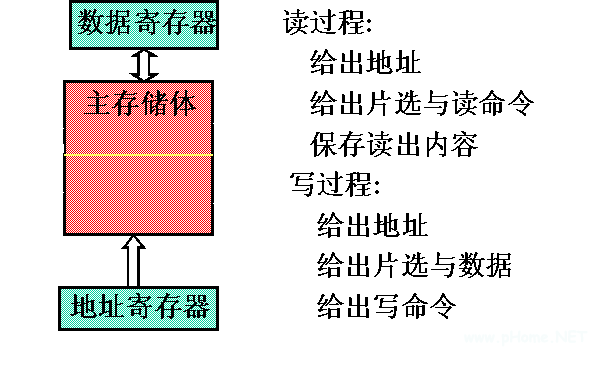
(2) Connection of main memory to CPU and peripheral devices
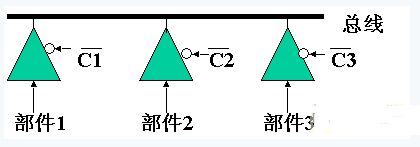
Is connected through the address bus, data bus, control bus, see the following figure
Main memory and CPU connection
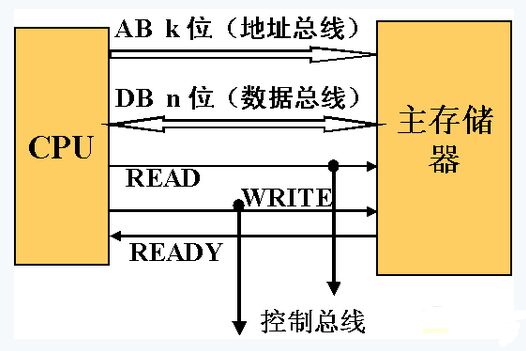
â—Ž The address bus is used to select a memory cell of the main memory. If the bit number of the address bus is k, the maximum addressable space is 2k. If k=20, you can access 1MB of storage unit.
â—Ž Data bus is used to transfer data between various functional components of the computer.
â—Ž The control bus is used to indicate the duty cycle of the bus and the time at which the input/output is completed.
(3) Main memory classification
â—Ž Long and short points according to information storage: ROM and RAM
â—Ž According to the production process: static memory and dynamic memory
Static Memory (SRAM): Fast read/write speed, high production cost, and mostly used for small-capacity cache memories.
Dynamic Memory (DRAM): slower read/write speed, high integration, low production cost, and mostly used for main memory with large capacity.
The main performance comparison between static memory and dynamic memory is as follows:
Comparison of static and dynamic memory chip characteristics
SRAM DRAM
Store information trigger capacitor
Destructive readout
Need to refresh, don't need
Send the row address and send it twice at the same time
Running fast
Low integration
Calorific value
Storage cost
Periodic refresh of dynamic memory: When no read/write operation is performed, each unit of the DRAM memory is in a power-off state. Due to the existence of leakage, the charge stored in the capacitor CS will slowly leak out, and this must be supplemented periodically. It is called a refresh operation.
2. Memory principle and read and write process of dynamic memory
(1) The composition of dynamic memory: a single MOS tube is used to store one bit of binary information. The information is stored in the parasitic capacitance CS of the source of the MOS transistor.
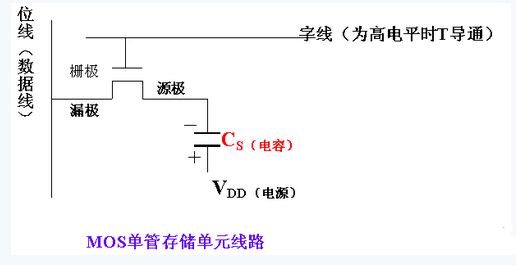
â—Ž When writing data: The word line is high level and T is turned on.
When writing "1", the bit line (data line) is low, and VDD (power) will charge the capacitor.
When “0†is written, the bit line (data line) is high. If the capacitor stores a charge, it will cause the capacitor to discharge, indicating that “0†is stored.
â—Ž When reading data: first make the bit line (data line) high. When the word line is high, T turns on. If the capacitor originally stores charge (is "1"), the capacitor will discharge. This will cause the data line potential to go from high to low; if the capacitor does not store charge (is "0"), the data line potential will not change. By detecting the change in potential on the data line, it is possible to distinguish whether the read data is 1 or 0.
note
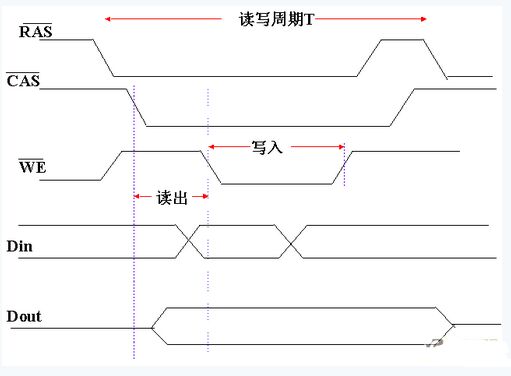
A read operation causes the charge stored in the capacitor to be lost, and is therefore a destructive read. In order to maintain the original memory content, a write operation must be followed immediately after the read operation, which is called a precharge delay.
2 Provide an address to the memory unit of the dynamic memory, which is the first line address and then the column address. The reason is that the dynamic memory must be refreshed periodically (such as 2ms). The refresh is not word-by-word processing, but each time a row is refreshed, that is, the energy of all the memory cells connected to the same row is supplemented once.
3 The readout signal on the bit line of the dynamic memory is very small, and must be connected to the sense amplifier, usually implemented by a flip-flop line.
4 The row address and column address latches inside the memory chip accept row and column addresses in succession.
The timing relationship of 5RAS, CAS, WE, Din, Dout is as follows:
3. The composition and design of the internal memory of the teaching computer
(1) Storage principle of static memory and internal structure of chip (P207)
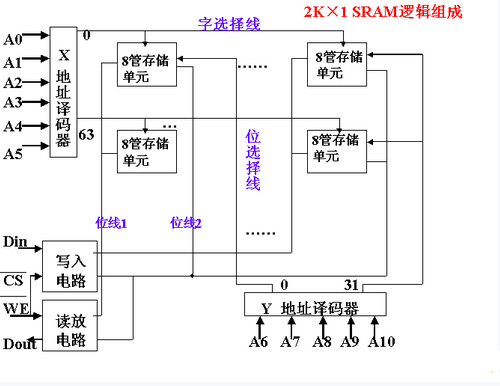
(2) The composition and design of the memory in the teaching computer
â—Ž Address bus: It is recorded as AB15~AB0, which is driven by the address register AR. The address register AR only receives the information output by the ALU.
â—Ž Control bus: The signal of the control bus is given by the decoder 74LS139. The function is to indicate the type of bus cycle:
※ Memory write cycle is marked with MMW signal
※ Memory read cycle is marked with MMR signal
※ Peripheral (interface) write cycle is marked with IOW signal
※ Peripheral (interface) read cycle is marked with IOR signal
※ Memory is marked with MMREQ signal for work
※ Peripherals are marked with IOREQ signal at work
※Write control cycle is marked with SWA signal
â—Ž Data bus: divided into two parts: internal data bus IB and external data bus DB. Mainly complete the data transfer between the various functional components of the computer.
The core technology of the design bus is to ensure that only one set of data can be sent to the bus at any time, while allowing one or more components to simultaneously accept information on the bus. The circuit used is typically a three-state gate.
â—ŽSystem clock and timing: The teaching machine crystal oscillator is 1.8432MHz. After dividing by 3, the 614.4KHz clock is used as the system master clock to make the CPU, memory and IO run synchronously.
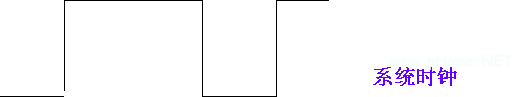
Some registers inside the CPU complete the acceptance of data with the rising edge at the end of the clock, while the general-purpose registers are received with low level. In memory or I/O read and write operations, each bus cycle consists of two clocks. The first clock, called the address time, is used to transfer the address. The second clock, called the data time, is used to read and write data.
â—Ž static memory word slot expansion:
The internal memory of the teaching computer is implemented by a static memory chip, which is composed of a 2K word ROM area and a 2K word RAM area. The memory word is 16 bits long and is addressed by word.
The ROM is extended by the 74LS2716 read-only memory ROM (2048 memory cells per chip, each bit is 8-bit binary bit). Address allocation: 0 ~ 2047
The RAM is extended by the 74LS6116 random access RAM (2048 memory cells per block, 8 bits per cell). Address allocation: 2048 ~ 4095
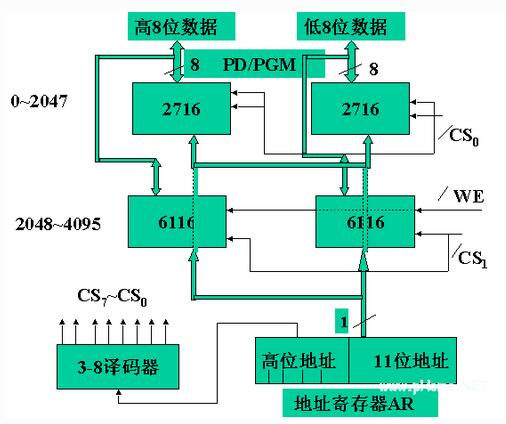
Static memory word, bit extension
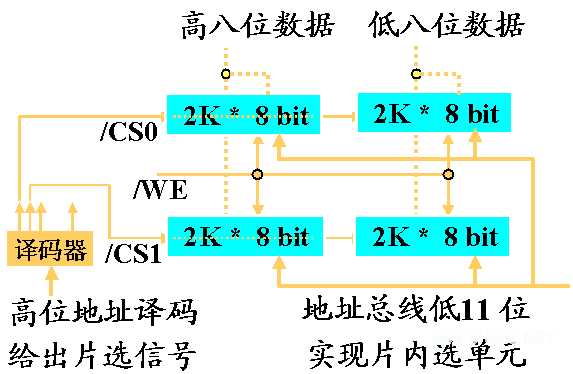
Main memory read and write process
Static memory address assignment:
To access 2048 memory locations, the 11-bit address is used to send the lower 11-bit address of the address bus to the address pin of each memory chip; the upper bits of the address bus are decoded, and the decoded signal is sent to each memory chip. /CS pin,
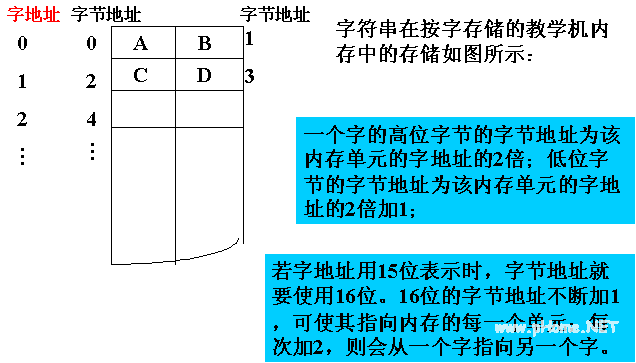
â—Ž Implement byte-by-byte read and write in word-addressable memory systems
4, main memory implementation and several techniques in the application
(1) Fast read and write technology of dynamic memory
â—Ž fast page work technology (fast read and write technology of dynamic memory)
When reading and writing the data of the same line of dynamic memory, the row address will remain unchanged after being locked for the first time. When reading and writing data in multiple columns of the row, only the column address can be latched, and the latch is omitted. The time of the row address speeds up the read and write speed of the main memory.
â—ŽEDO (Extended Data Out) technology
In the fast page type working technology, the data latching line of the data output part is added, and the effective holding time of the output data is prolonged, so that the address signal is changed, and the correct reading data can still be obtained, and the address feeding time can be further shortened. Speed ​​up the read and write speed of the main memory.
(2) Parallel read and write technology of main memory
It refers to the technique used to read multiple main memory words in one duty cycle (or longer) of the main memory.
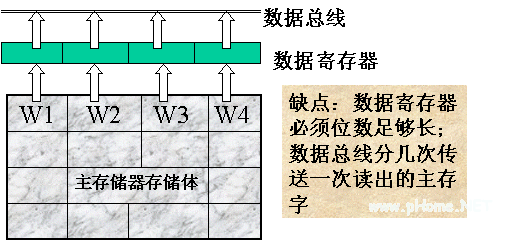
Solution 1: An integrated multi-word structure, that is, increasing the data bits included in each main memory unit to store several main memory words at the same time, and reading several main memory words at the same time for each read operation.
Scheme 2: Multi-body cross-addressing technology, the main memory is divided into several main body that can be read and written independently, and the word length is a main memory word, and each memory is read and written separately; Run to provide higher read and write speeds than a single bank.
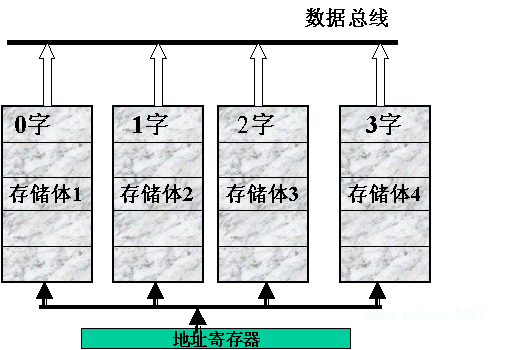
There are two ways to read and write:
â—Ž Start all main memory read or write at the same read and write cycle.
â—Ž Let the main memory read or write sequentially, that is, each memory word read out in sequence can be sequentially transferred through the data bus without setting a special data buffer register. Secondly, the method of cross-addressing is adopted. Several memory words of consecutive addresses are sequentially allocated in different banks, because according to the local characteristics of the program running, the probability of reading and writing adjacent main words in a short time is greater.

(3) Memory support for group data transfer
The so-called group data transfer is that after the address bus transmits the address once, it can continuously transmit a plurality of data on the data bus. Originally, it takes two clock cycles to transmit data once: first send an address first, followed by a data transfer, that is, to transmit N data, it is necessary to use 2N bus clock cycles, and the group data transmission mode only uses N+1. Bus cycle time.
To achieve a group data transfer mode, not only the CPU must support this mode of operation, but also the main memory can provide a high enough data read and write speed, which is often achieved by means of a multi-body structure of the main memory and EDO support of the dynamic memory.
The WiFi 6 Outdoor Wireless AP is a wireless access point for outdoor environments that uses the latest WiFi 6 technology to deliver higher speeds, more capacity, and better performance. The benefits of WiFi 6 Outdoor Wireless AP are described in detail and analyzed in depth below.
First, higher speed:
WiFi 6 Outdoor Wireless AP uses the latest 802.11ax standard to support higher data transfer rates. Compared to the previous WiFi 5 technology, WiFi 6 can achieve higher peak speeds, up to 10Gbps. This means users can enjoy faster download and upload speeds, smoother online gaming and high-definition video viewing experiences.
Second, larger capacity:
The WiFi 6 Outdoor Wireless AP uses OFDMA technology to divide wireless signals into multiple sub-channels to serve multiple devices at the same time. Compared to the previous WiFi 5 technology, WiFi 6 can connect more devices at the same time, providing greater network capacity. This is important for modern homes and businesses as the number of devices we have increases and the demand for network capacity increases.
Third, better performance:
The WiFi 6 Outdoor Wireless AP introduces an improved version of MU-MIMO technology that can communicate with multiple devices simultaneously. This means that users can enjoy a more stable and reliable wireless connection, whether in a home environment or an enterprise environment. In addition, WiFi 6 also introduces BSS Coloring technology, which can reduce interference between neighboring networks and improve network performance and throughput.
4. Lower latency:
The WiFi 6 Outdoor Wireless AP uses Target Wake time (TWT) technology to synchronize the wake time of the device with the time of the wireless transmission. This means the device can wake up quickly when it is needed and go to sleep when it is not, reducing latency in wireless transmission. This is important for real-time applications, such as online gaming and video conferencing, to provide a better user experience.
Five, better security:
WiFi 6 Outdoor Wireless AP introduces the WPA3 security protocol, which provides stronger encryption and authentication mechanisms to protect users' wireless networks from hackers and malicious attacks. In addition, WiFi 6 also supports more security features such as encryption for OFDMA and MU-MIMO, as well as stricter access control and user authentication.
Six, better coverage:
The WiFi 6 Outdoor Wireless AP uses more advanced antenna design and signal processing technology to provide wider wireless coverage. This is very important for outdoor environments, which can cover a larger area and meet the needs of users for wireless networks.
In summary, the WiFi 6 Outdoor Wireless AP offers higher speeds, more capacity, better performance, lower latency, better security, and better coverage. It is an advanced wireless access point for outdoor environments that can meet the needs of users for high-speed, high-capacity, high-reliability wireless networks. As the number of Wireless devices increases and the requirements for network performance continue to increase, WiFi 6 Outdoor Wireless AP will become an important part of the wireless network of the future.
WiFi 6 Outdoor Wireless AP,oem WiFi 6 Outdoor Wireless AP,WiFi 6 Outdoor Wireless AP oem,best WiFi 6 Outdoor Wireless AP
Shenzhen MovingComm Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.movingcommtech.com