The current probe measures the magnetic field generated by the movement of electrons within the wire. Within the current probe's range specification, the flux field around the wire is converted to a linear voltage output that can be displayed and analyzed on an oscilloscope or other measuring instrument. The flux field can be accurately measured by completely winding the wire around the probe core (core and solid). Split core probes are very convenient, they can be clipped on the wire without having to disconnect. Solid-core current transformers (ct) are designed for permanent or semi-permanent installations. They are small in size and provide very high frequency response for ultrafast, low amplitude current pulses and ac signals.
How the current probe works when testing DC and low frequency ACWhen the current clamp is closed and a current-carrying conductor is centered, a magnetic field will appear in response. These magnetic fields deflect the electrons in the Hall sensor and produce an electromotive force at the output of the Hall sensor. The current probe generates a reverse (compensated) current according to this electromotive force to the coil of the current probe, so that the magnetic field in the current clamp is zero to prevent saturation. The current probe measures the actual current value based on the reverse current. In this way, it is possible to measure large currents very linearly, including AC and DC mixed currents.

How the current probe works when testing DC and low frequencies
How the current probe works when testing high frequenciesAs the frequency of the measured current increases, the Hall effect gradually decreases. When measuring a high-frequency alternating current without a DC component, most of the coil is directly induced by the strength of the magnetic field. At this point, the probe acts like a current transformer. The current probe directly measures the induced current, not the compensation current. The output of the amplifier provides a low-impedance ground loop for the coil.
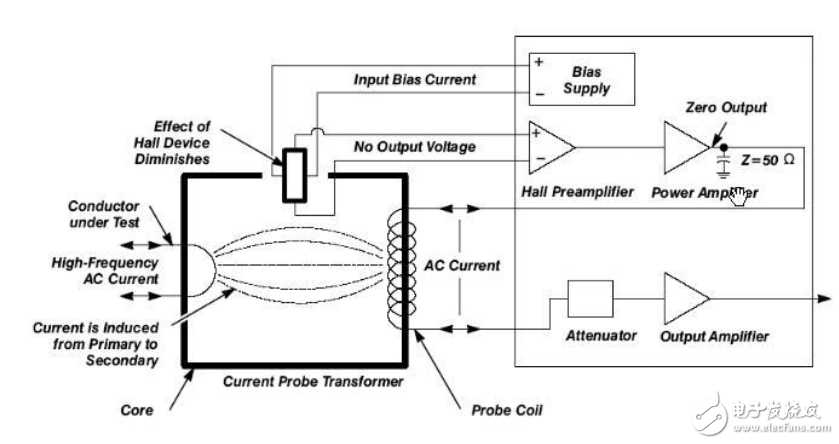
How the current probe works when testing high frequencies
How the current probe works in the crossover areaWhen the current probe operates in the high-low frequency crossover region of 20KHz, part of the measurement is achieved by the Hall sensor and the other part is realized by the coil.
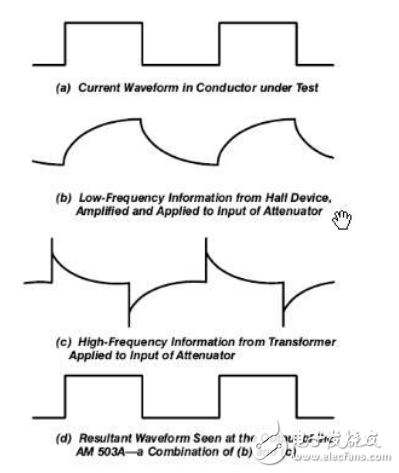
How the current probe intersection area works
Splitter: To divide the input signal equally among the different sets; At the same time, these televisions are isolated from each other. Usually there are :2 distribution (divided in two), 3 distribution, etc. Cable TV also has a distributor, which is different from a distributor. The branching device transfers some of the energy to the next stage. Branch devices are often used in cable television networks
DAB Spliter,DAB Spliter SMA,DAB Spliter for Car,DAB Spliter Signal Amplifier,AM /FM DAB Antenna
Yetnorson Antenna Co., Ltd. , https://www.yetnorson.com