Human-computer interaction, human-computer interaction (English: Human–Computer InteracTIon or Human–Machine InteracTIon, referred to as HCI or HMI) is a study of the interaction between the system and the user. The system can be a wide variety of machines or computerized systems and software. The human-computer interaction interface usually refers to the part that is visible to the user. The user communicates with the system through the human-computer interaction interface and operates. Small as a radio play button, as large as the dashboard on the plane, or the control room of the power plant. The design of the human-computer interaction interface should include the user's understanding of the system (ie, the mental model), which is for system availability or user-friendliness.
The concept of human-computer interaction:Definition 1: Discipline on the design, evaluation, implementation, and related phenomena of interactive computer systems [ACM]
Definition 2: Research subjects, computers, and the disciplines in which they interact. The purpose of learning human-computer interaction is to make computer technology better serve humans [Alan Dix]
Definition 3: Learning and practice about usability is about understanding and building software and technology that users are happy to use, and discovering the effectiveness of products when they are used [Carroll]
main content:1. Method and process of interface design. That is, under the premise of given tasks and users, the optimal interface is designed to meet the given constraints, and the attributes such as easy-to-learn and usability are optimized.
2. Interface implementation method. Such as software toolkits and library functions, as well as various other efficient development methods, etc.
3. Interface analysis and evaluation techniques.
4. Develop new interfaces and interactive technologies.
5. Construct an interaction-related description model and prediction model
1. A framework is a structure that provides understanding or definition. It can help people structure the design process, recognize the main issues in the design process, and help define the areas involved in the problem. 2. Execution/evaluation activity cycle EEC: Activities The four basic components: the goal (what to do), the execution (the action that must be performed to achieve the goal), the objective factors (the objective conditions that must be considered when performing the activity), and the assessment (used to measure the outcome of the activity between the target objectives) difference)
Seven phases: establishing goals, forming operational intentions, clarifying sequence of actions, performing actions, sensing system status, interpreting system status, and evaluating system status against targets
Execution barrier: The difference between the action made by the user to achieve the goal and the action allowed by the system. The gap between the actual performance of the system state and the user's expectations 3. Extended EEC framework
(1) Four components of an interactive system: system (S), user (U), input (I), output (O)
(2) where input and output form the interface
(3) The implementation phase consists of three translation processes:
Definition: The user elaborates on a certain target and then performs coordination and link execution through the input language: the input language is converted into a kernel language, indicating the operation performance of the system to be executed: the system uses the output language to express the execution result of the kernel language.
(4) Process of the assessment phase
Observation: The user compares the output to the original target to evaluate the result of the interaction
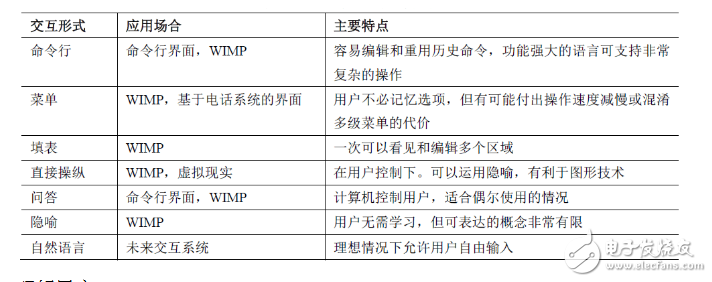
Q&A interface: The interaction between the person and the computer is realized by asking the user a series of questions (the Web questionnaire is a typical application using the question and answer method, and the user should be allowed to easily cancel the option of one of the interfaces)
Advantages: low memory requirements; each interface is self-explanatory; the task flow is represented by a simple linear; suitable for novice users.
Disadvantages: requires effective input from the user; requires the user to be familiar with interface control; the error correction process may be tedious. Metaphor interface:
Essence: Create a new set of knowledge based on the user's existing knowledge, realize the perceptual connection between the visual cues and system functions of the interface, and help users to change from novice users to expert users.
Advantages: intuitive and vivid; no need to learn.
Disadvantages: Not scalable; different users may have different associations for the same thing; tightly bound our ideas and the physical world; finding the right metaphor may be difficult.
130W Medical Power Supply,130W Medical Device Power Supply,130W Medical Power Adapter,130W Rade Power Supplies
Shenzhen Longxc Power Supply Co., Ltd , https://www.longxcpower.com